 15 citations,
April 2003 in “Journal of dermatology”
15 citations,
April 2003 in “Journal of dermatology” Alopecia areata causes hair loss due to an immune attack on hair follicles, influenced by genetics and environment.
13 citations,
October 2006 in “Pediatrics in review” Early puberty is more common in girls and African-American children, possibly due to nutrition, obesity, stress, and environmental factors, and is treated with hormone therapy.
3 citations,
April 2019 in “Stem cells international” Markers CRABP1, Nestin, and Ephrin B2 are present in skin cancer environments and may influence their development.
 2 citations,
August 2012 in “Cell Stem Cell”
2 citations,
August 2012 in “Cell Stem Cell” The study showed that some hair follicle stem cells wake up to grow hair while others stay asleep, and that the environment around them is important for hair growth.
 2 citations,
January 2008 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2008 in “Elsevier eBooks” Humans have limited regenerative abilities, but new evidence shows the adult brain and heart can regenerate, and future treatments may improve this by mimicking stem cell environments.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Foods”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Foods” Mushrooms offer benefits for food, energy, and water security, and have potential uses in health and environmental applications.
 1 citations,
March 2021 in “Dermatological reviews”
1 citations,
March 2021 in “Dermatological reviews” AGA, a common hair loss, is caused by genetics, hormones, age, and environmental factors.
 1 citations,
May 2019 in “Veterinarski arhiv”
1 citations,
May 2019 in “Veterinarski arhiv” The yeast found in a sea lion's skin lesion was almost identical to that on healthy skin, suggesting environmental factors may affect fungal growth and the cause of the lesion is unclear.
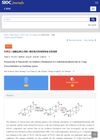 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry” Using K2S2O8 as an oxidizing agent in a specific condition, we can make Finasteride with 96.3% yield and 99.6% purity. This method is also good for other compounds and is environmentally friendly.
 1 citations,
October 2013
1 citations,
October 2013 Different ectodermal organs like hair and feathers regenerate differently, with specific stem cells and signals involved in their growth and response to the environment.

Androgenetic alopecia, or hair loss, is caused by a mix of genetics, hormones, and environment, where testosterone affects hair growth and causes hair to become smaller and grow for a shorter time.

Skin changes throughout life, from development before birth to aging effects like wrinkles, influenced by both genetics and environment.
January 2011 in “Companion Animal” Dermatophytosis in cats is a contagious skin disease that requires treating the infected cat, other pets, and the environment.

Hair loss in African American women, caused by hair care, genetics, and environment, needs more research for better treatment.
 September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Male pattern baldness affects 38.52% of Asian men in Bangkok, increasing with age and possibly linked to environment and diet.
 December 2022 in “Rossiiskii Zhurnal Kozhnykh i Venericheskikh Boleznei”
December 2022 in “Rossiiskii Zhurnal Kozhnykh i Venericheskikh Boleznei” Androgenic alopecia in men is mainly linked to family history, hormonal imbalances, and metabolic issues, but can also be influenced by lifestyle habits, environmental factors, and deficiencies in certain vitamins and microelements like copper.
 March 2019 in “Chinese Journal of Dermatology”
March 2019 in “Chinese Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss, known as androgenetic alopecia, is mainly caused by genetics, but also by hormone imbalances, shrinking hair follicles, inflammation, and environmental factors.
 295 citations,
March 2016 in “Life Sciences”
295 citations,
March 2016 in “Life Sciences” Air pollution worsens skin diseases and aging by causing inflammation and oxidative stress.
 253 citations,
March 2006 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism”
253 citations,
March 2006 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism” Exposure to too much androgen before birth might cause polycystic ovary syndrome later in life.
221 citations,
July 2012 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” BMAL1 controls skin cell growth and UV damage risk, peaking at night.
 175 citations,
November 2009 in “PLOS ONE”
175 citations,
November 2009 in “PLOS ONE” Women look young for their age due to larger lips, less sun damage, and genes that prevent gray hair and wrinkles.
162 citations,
October 2014 in “Autoimmunity reviews” Alopecia areata is caused by the immune system attacking hair follicles.
160 citations,
July 2008 in “Experimental dermatology” Melatonin protects the skin by scavenging free radicals and repairing DNA damage.
 150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology”
150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology” The document concludes that more research is needed to better understand and treat primary cicatricial alopecias, and suggests a possible reclassification based on molecular pathways.
 148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing patchy hair loss, often with other autoimmune disorders, but its exact causes are unknown.
 96 citations,
September 2017 in “Analytica Chimica Acta”
96 citations,
September 2017 in “Analytica Chimica Acta” Hair elemental analysis could be useful for health and exposure assessment but requires more standardization and research.
 92 citations,
August 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
92 citations,
August 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Newborn mouse skin cells can grow hair and this process can be recreated in adult cells to potentially help with hair loss.
40 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatrics in review” Puberty involves complex hormonal changes, varies by gender and ethnicity, and requires careful monitoring for abnormalities.
 40 citations,
January 2010 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
40 citations,
January 2010 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Certain diets can affect skin conditions, but more research is needed to understand these relationships fully.
39 citations,
January 2018 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Acne and hidradenitis suppurativa have different causes and risk factors, but both are driven by inflammation and may benefit from treatments targeting interleukin-1.






















