 10 citations,
June 2019 in “Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine”
10 citations,
June 2019 in “Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine” Scientists successfully grew new hair follicles in regenerated mouse skin using mouse and human cells.
 6 citations,
February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
6 citations,
February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A new model using mice with human hair follicles helps better understand hair loss from chemotherapy.
[object Object]  April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Stem cells can create hair follicles, potentially treating permanent hair loss, and healthy skin and hair depend on mitochondrial function and special fats.
 17 citations,
February 2019 in “PubMed”
17 citations,
February 2019 in “PubMed” Stem cells can help regenerate hair follicles.
 159 citations,
July 2006 in “Endocrine Reviews”
159 citations,
July 2006 in “Endocrine Reviews” Estrogens significantly influence hair growth by interacting with receptors in hair follicles and may help regulate the hair growth cycle.
 4 citations,
April 2021 in “Experimental Dermatology”
4 citations,
April 2021 in “Experimental Dermatology” Antibiotics might affect hair growth by changing the bacteria in hair follicles.
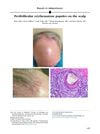 January 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The woman has a type of scarring hair loss with red bumps around hair follicles.
 December 2015 in “Vascular Pharmacology”
December 2015 in “Vascular Pharmacology” Hair papilla cells are crucial for blood vessel development in hair follicles, affecting hair growth and loss.
 18 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
18 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Certain cells outside the hair follicle's bulge area can quickly regenerate damaged hair follicles, potentially helping to reduce hair loss from cancer treatments.
 50 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
50 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Estrogens generally inhibit hair growth and improve skin quality, but their exact effects on hair follicles are complex and not fully understood.
November 2022 in “Regenerative Therapy” Advancements in tissue engineering show promise for hair follicle regeneration to treat hair loss.
14 citations,
April 2021 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Mesenchymal stem cells may help treat hair loss by improving hair cell growth and reducing inflammation.
 47 citations,
January 2019 in “Nature communications”
47 citations,
January 2019 in “Nature communications” Polyamines help fix DNA damage accurately in cells.
 6 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of dermatology”
6 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of dermatology” Immune checkpoint inhibitors used in cancer therapy can cause hair loss, and understanding this can help manage the side effect.
 34 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
34 citations,
February 2012 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The research found specific signs to diagnose alopecia areata incognito and noted patients generally regrow hair after steroid treatment.
 32 citations,
January 1997 in “Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 1997 in “Dermatology” Telogen effluvium is a hair loss condition with acute cases resolving quickly and chronic cases potentially lasting longer, sometimes requiring treatment.
 21 citations,
November 2009 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
21 citations,
November 2009 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The document suggests that certain protein deficiencies and scalp blistering in Epidermolysis Bullosa may cause hair loss.
 17 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology”
17 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology” A man experienced hair loss from radiotherapy, which can be temporary or permanent depending on radiation dose, with potential treatments available.
 8 citations,
January 2015 in “International journal of trichology”
8 citations,
January 2015 in “International journal of trichology” A woman's total hair loss was linked to a Borrelia infection and was reversed with appropriate treatment.
 7 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
7 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Two siblings both had a rare case of alopecia areata at the same time.
 3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” Possible causes of female hair loss include androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, cicatricial alopecia, and alopecia areata incognita; diagnosis and treatment require dermoscopy and histopathology.
 2 citations,
March 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
March 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology” The "color-transition sign" helps tell apart alopecia areata incognita from telogen effluvium by looking at hair color changes.
 1 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Chemotherapy patients don't all lose their hair due to factors like hair growth rates, age, genetics, and the type of drugs used.
 February 2023 in “International Journal of Medical Arts”
February 2023 in “International Journal of Medical Arts” Trichloroacetic acid is a safe and effective treatment for hair loss in alopecia areata patients.
 June 2019 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
June 2019 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Alopecia in patients with epidermolysis bullosa varies in severity and is often caused by skin blistering or trauma.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A new peptide, FOL-005, may help treat excessive hair growth by reducing a hair growth promoter, FGF7.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blood cells turned into stem cells can become skin cells similar to normal ones, potentially helping in skin therapies.
 September 1998 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
September 1998 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Autoimmune and inflammatory processes are involved in both scarring and non-scarring types of hair loss.
[object Object]  290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, stress, and diet, and may be prevented by a high soy oil diet.
 232 citations,
October 2015 in “International journal of molecular sciences”
232 citations,
October 2015 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Stem cells are crucial for skin repair and new treatments for chronic wounds.




























