 23 citations,
November 2011 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
23 citations,
November 2011 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Hair loss is a rare but recognized symptom of pemphigus vulgaris, with patients usually regrowing hair after treatment.
 155 citations,
June 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
155 citations,
June 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Lichen planus is a skin condition that can resolve on its own, is linked to hepatitis C, and increases the risk of skin cancer.
 6 citations,
September 1990 in “International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics”
6 citations,
September 1990 in “International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics” The skin condition PUPP usually gets better on its own after giving birth and is unlikely to happen again in future pregnancies.
132 citations,
April 2005 in “Gastroenterology” A gluten-free diet significantly improves skin and health issues in people with dermatitis herpetiformis, a skin condition linked to celiac disease.
 39 citations,
October 2018 in “Lupus Science & Medicine”
39 citations,
October 2018 in “Lupus Science & Medicine” Different types of hair loss in lupus need careful diagnosis for proper treatment.
 1 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Pathology of Nepal”
1 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Pathology of Nepal” Testing hair roots with a special dye is a simple, non-invasive way to check disease progress in pemphigus vulgaris patients.
 106 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
106 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Correct skin biopsy techniques are crucial to avoid misdiagnosis of skin diseases.
 November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Most patients with blistering skin disorders in South India had bullous pemphigoid and often had other conditions like hypertension and diabetes.
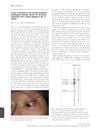 7 citations,
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
February 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A woman with a rare autoimmune disorder had a blister on her eye and unique immune reaction, which was effectively treated with medication.

A thorough skin history and examination are essential for diagnosing and treating skin conditions effectively.
 273 citations,
May 2017 in “The Lancet”
273 citations,
May 2017 in “The Lancet” Some drugs can cause rare but potentially deadly skin reactions, and early treatment and avoiding the drug again are key.
 7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Stopping imipramine reduced the woman's hair loss.
 December 2004 in “Medicine”
December 2004 in “Medicine” Pregnancy can cause skin changes and may affect pre-existing skin conditions, with some treatments not safe for use during pregnancy.
 20 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology”
20 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” Different skin diseases show unique patterns of skin cell separation, cell death, and granular layer changes.
 15 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
15 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Hair loss in systemic lupus erythematosus patients is unique and improves with treatment.
 208 citations,
July 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
208 citations,
July 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Pregnancy can cause various skin changes and diseases, with PUPPP being the most common skin condition specific to pregnancy.
 1 citations,
December 2012 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
1 citations,
December 2012 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The health of the sentinel lymph node is the best indicator of survival for patients with thick skin cancer.
 30 citations,
September 2005 in “Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology”
30 citations,
September 2005 in “Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology” The document concludes that treating tough skin disease in lupus involves sun protection, steroids, antimalarials, and various other therapies chosen based on individual risks and benefits.
 March 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
March 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The document concludes that there have been significant improvements in diagnosing and treating skin diseases, including melanoma, with new techniques and therapies.
 41 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
41 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Men with Frontal fibrosing alopecia typically lose hair on the front scalp and sometimes on sideburns and upper lip, with treatments showing varied success.
 59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine”
59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine” There are still challenges in diagnosing and treating chronic skin diseases, but there is hope for future improvements.
 76 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
76 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The conclusion is that certain scalp tissue changes are characteristic of lichen planopilaris, with mucinous perifollicular fibroplasia being a new feature for diagnosis.
 26 citations,
June 2012 in “The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India”
26 citations,
June 2012 in “The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India” Most skin changes during pregnancy are harmless and temporary, but some can risk the fetus and need careful treatment.
 149 citations,
July 2002 in “Dermatologic clinics”
149 citations,
July 2002 in “Dermatologic clinics” Patients with certain skin symptoms and high ANA titers should be monitored for potential systemic lupus.
 January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hair loss is common in autoimmune diseases and can be an early sign of the condition, often requiring prompt treatment to prevent permanent damage.
 January 2009 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2009 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that managing skin conditions during pregnancy is important and requires specialized care.
1 citations,
January 2018 in “Cogent Medicine” Careful management of steroid use is crucial in pregnant women with bullous pemphigoid to avoid complications like Cushing syndrome.
 3 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
3 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document suggests that severe hair loss in SLE patients may be an early sign of scalp DLE, treatable with immunosuppressive therapy.
 5 citations,
August 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
5 citations,
August 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Iron deficiency might contribute to hair loss in women.
 1 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” The convention discussed various skin conditions and treatments, and highlighted the importance of vaccinations for patients on immune-altering medications.




























