 January 2016 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
January 2016 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” A substance called prostaglandin D2 is found more in bald scalps and it stops hair from growing. Blocking its receptor could potentially treat hair loss.
 May 2012 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
May 2012 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Prostaglandin D2, found in higher levels in bald scalps, stops hair growth, suggesting that blocking its receptor could potentially treat hair loss.
 July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” The document concludes that understanding hair follicle histology and the hair cycle is crucial for diagnosing alopecia.
 November 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
November 2024 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Stem cells from umbilical cords can help regrow hair in mice with hair loss.
54 citations,
May 2001 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Excessive putrescine causes hair loss in transgenic mice by disrupting hair follicle development.
 May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” A shampoo with caffeine and adenosine may help prevent hair loss and thicken hair.
December 2023 in “Animals” The study mapped yak skin cells to understand hair growth better.
14 citations,
April 2021 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Mesenchymal stem cells may help treat hair loss by improving hair cell growth and reducing inflammation.
 90 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
90 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Growth factors are crucial for hair development and could help treat hair diseases.
 72 citations,
June 2001 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
72 citations,
June 2001 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” S100A4 and S100A6 proteins may activate stem cells for hair follicle regeneration and could be potential targets for hair loss treatments.
 52 citations,
September 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
52 citations,
September 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Ginseng and its compounds may help hair growth and prevent hair loss, but more human trials are needed to confirm this.
 39 citations,
March 2018 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
39 citations,
March 2018 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Androgens may block hair growth signals, targeting this could treat hair loss.
 33 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
33 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” The document explains hair biology, the causes of hair loss, and reviews various hair loss treatments.
 27 citations,
August 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
27 citations,
August 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Researchers found new genes involved in hair growth, which could help develop new hair treatments.
 10 citations,
February 2008 in “Photochemistry and photobiology”
10 citations,
February 2008 in “Photochemistry and photobiology” Vitamin D receptor can control the hairless gene linked to hair loss even without vitamin D.
 April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research found genes that may protect certain scalp cells from hair loss.
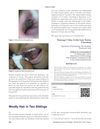 January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Two siblings have a rare genetic condition causing curly, coarse hair.
 58 citations,
January 2006 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
58 citations,
January 2006 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” High levels of testosterone and 5α-DHT can lead to cell death in cells important for hair growth.
 39 citations,
March 2009 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
39 citations,
March 2009 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Apigenin may help promote hair growth and could treat hair loss.
 26 citations,
March 2015 in “Phytotherapy Research”
26 citations,
March 2015 in “Phytotherapy Research” Forsythiaside-A, a natural substance, can protect against hair loss and is more effective than current treatments, potentially making it a good option for hair loss treatment.
 24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that eyelash trichomegaly, which is the abnormal growth of eyelashes, can be present from birth, caused by diseases, or result from certain medications.
 June 2021 in “Journal of emerging technologies and innovative research”
June 2021 in “Journal of emerging technologies and innovative research” Onion and Aloe vera can help protect hair from damage caused by hair dyes.
 May 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
May 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Scientists developed tools to observe hair regeneration in real time and assess skin health, using glowing mice and light-controlled genes.
 September 2003 in “Clinics in Family Practice”
September 2003 in “Clinics in Family Practice” Different hair diseases affect people during childbearing years, with treatments ranging from medication to psychological support.
 421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss with no cure and treatments that often don't work well.
 100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today”
100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today” Growth factors and cytokines are important for hair growth and could potentially treat hair loss, but more research is needed to overcome challenges before they can be used in treatments.
 98 citations,
June 2008 in “Human mutation”
98 citations,
June 2008 in “Human mutation” A genetic change in the EDAR gene causes the unique hair traits found in East Asians.
 97 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
97 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The human hair follicle can store topical compounds and be targeted for drug delivery with minimal side effects.
 89 citations,
September 2010 in “Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics”
89 citations,
September 2010 in “Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics” The document concludes that understanding the genes and pathways involved in hair growth is crucial for developing treatments for hair diseases.
 81 citations,
February 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
81 citations,
February 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Minoxidil boosts hair growth by activating PGHS-1.


























