 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with limited and variable treatment effectiveness.
 July 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that various hypersensitivity diseases in horses can be diagnosed and treated with methods like immunotherapy and medication, and early aggressive treatment is crucial for severe diseases like equine cutaneous pythiosis.
 November 2012 in “The Journal of Urology”
November 2012 in “The Journal of Urology” Certain gene variants may raise the risk of prostate enlargement, but taking NSAIDs could reduce this risk.

Obesity is linked to many gastrointestinal diseases and needs more research for treatment development.
 January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia areata is a reversible, autoimmune-related hair loss that can have significant emotional impact and uncertain treatment effectiveness.
 January 2006 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2006 in “Elsevier eBooks” Cats with Feline Symmetrical Alopecia can regrow hair with proper treatment based on the specific cause, including diet, medication, or stress management.
 August 2020 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
August 2020 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” PRP injections improve hair density in men with hair loss, with few short-term side effects.
 23 citations,
September 2021 in “Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology”
23 citations,
September 2021 in “Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology” Testosterone's effects on COVID-19 are unclear and need more research.
May 2021 in “Medicina internă” High-dose corticosteroid treatment helped improve symptoms in a patient with Adult Onset Still Disease.
70 citations,
September 2017 in “Expert opinion on therapeutic patents” The review suggests that while many AKR1C3 inhibitors show promise for treating certain cancers, more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness in humans.
3 citations,
August 2018 in “Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management” Corticosteroid therapy for alopecia areata can cause severe hip bone damage.
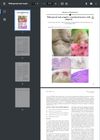 November 2022 in “JAAD case reports”
November 2022 in “JAAD case reports” A man with skin and hair symptoms improved partially with specific treatment.
38 citations,
January 2017 in “PPAR Research” PPAR-γ helps control skin oil glands and inflammation, and its disruption can cause hair loss diseases.
9 citations,
May 2022 in “Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience” Mesenchymal stromal cell therapies show promise for treating various diseases but need more research and standardization.
 9 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
9 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells are important for immunity and tolerance, affect hair growth and wound healing, and their dysfunction can contribute to obesity-related diseases and other health issues.
8 citations,
January 2019 in “Turkish journal of medical sciences” Ischemic modified albumin could be a new indicator of oxidative stress in people with alopecia areata.
466 citations,
June 2009 in “Experimental dermatology” We now understand more about what causes acne and this could lead to better, more personalized treatments.
286 citations,
August 2007 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease where T cells attack hair follicles.
256 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” There is no standardized treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa, and individualized plans are needed.
142 citations,
March 2019 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” Cannabinoids may help treat various skin conditions.
 29 citations,
March 2021 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
29 citations,
March 2021 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Testosterone may influence COVID-19 severity and outcomes.
24 citations,
December 2018 in “Inflammation and Regeneration” Phospholipase A2 enzymes play key roles in skin health and disease.
 21 citations,
November 2021 in “Biomolecules”
21 citations,
November 2021 in “Biomolecules” Eclipta prostrata is a medicinal plant that helps treat diseases, protects the liver and nerves, and promotes hair growth.
 18 citations,
June 2019 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
18 citations,
June 2019 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Acne can't be cured but can be managed with treatments like benzoyl peroxide and diet changes; it's costly and can lead to scarring and mental health issues.
 15 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology”
15 citations,
October 2021 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Natural volatiles and essential oils have health benefits and can enhance the effects of some medicines, but more research is needed to understand how they work and their possible side effects.
15 citations,
December 2018 in “International journal of environmental research and public health/International journal of environmental research and public health” EGCG may help treat alopecia areata by blocking certain immune responses and reducing specific harmful immune cells.
12 citations,
December 2010 in “Journal of thoracic oncology” New treatments for non-small cell lung cancer are being tested, with some already in use, focusing on immune response and targeting cancer cells, but side effects vary.
10 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Erosive pustular dermatosis in elderly people may be linked to aging immune systems and skin damage.
 9 citations,
December 2022 in “Phytomedicine”
9 citations,
December 2022 in “Phytomedicine” More high-quality research is needed to recommend flavonoids and saponins for clinical use.
8 citations,
October 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” MR antagonists may improve skin health and wound healing, especially in aging.















