 16 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
16 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition that needs more research for better treatments.

Alopecia Areata has no cure, treatments are limited, and the condition often recurs, but new therapies like JAK inhibitors show promise.
 8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Many patients with Alopecia Areata in Korea experience anxiety, depression, and reduced quality of life, which are often unrelated to the severity of hair loss.
 3 citations,
June 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that hair loss is complex, affects many people, has limited treatments, and requires more research on its causes and psychological impact.

Frontal fibrosing alopecia in men is often misdiagnosed and needs better diagnostic criteria and treatments.
 7 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Vitamin A may influence hair loss conditions like alopecia, but more research is needed to understand how.
 10 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering”
10 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering” Platelet-rich plasma can potentially improve hair regeneration by increasing follicular gene expression and hair growth activity.

Different hair and nail conditions can indicate health issues and have specific treatments; accurate diagnosis is crucial before treatment.
63 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry” Runx1 affects hair growth, cancer development, and autoimmune diseases in epithelial tissues.
 1 citations,
February 1988 in “The BMJ”
1 citations,
February 1988 in “The BMJ” The document explains different hair and scalp conditions, including common hair loss after pregnancy or illness, drug-induced hair loss, hereditary excessive hair growth, patterned baldness, autoimmune hair loss, and permanent loss due to skin disease, with generally limited treatment options.
 January 2025 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
January 2025 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Certain patient traits can predict better hair regrowth with baricitinib in severe alopecia areata.
 December 2022 in “Rossijskij žurnal kožnyh i veneričeskih boleznej”
December 2022 in “Rossijskij žurnal kožnyh i veneričeskih boleznej” New treatments for child hair loss due to immune issues are effective but not yet officially approved.
 September 2023 in “International journal of women’s dermatology”
September 2023 in “International journal of women’s dermatology” Certain hairstyles, diabetes, scalp infections, and vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of hair loss in Black women; more research is needed for better treatment.
 10 citations,
March 2014 in “Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation”
10 citations,
March 2014 in “Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation” Malondialdehyde-modified DNA may trigger an immune response in alopecia areata patients.
 8 citations,
January 2008 in “European Journal of Pediatrics”
8 citations,
January 2008 in “European Journal of Pediatrics” Children with autoimmune gastritis showed improved intestinal health over time and should be checked for other autoimmune conditions.
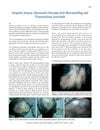 53 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
53 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Microneedling combined with triamcinolone can safely stimulate faster hair regrowth in people with Alopecia Areata.
 3 citations,
October 1982 in “Postgraduate Medicine”
3 citations,
October 1982 in “Postgraduate Medicine” Most types of hair loss can regrow naturally, but there are no effective cures for male pattern or age-related hair loss, and only limited options for females.
 October 2024 in “Reumatizam”
October 2024 in “Reumatizam” New treatments and understanding of skin lupus are emerging in 2024.
 May 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
May 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The meeting covered advances in understanding hair growth, causes of hair loss, and potential treatments.
 19 citations,
November 2011
19 citations,
November 2011 Using systemic drugs as creams for skin conditions shows promise, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness and safety.
 12 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
12 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Fox Fordyce disease might be more common in prepubertal girls than thought and can be managed with treatment.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Androgens increase growth factors in skin cells, which may lead to acne.
 191 citations,
May 2018 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
191 citations,
May 2018 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Alopecia areata is likely an autoimmune disease with unclear triggers, involving various immune cells and molecules, and currently has no cure.

No treatment alters the natural progression of alopecia areata, and effectiveness varies, with some possibly working better in children.
 18 citations,
January 2014 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii”
18 citations,
January 2014 in “Postępy Dermatologii i Alergologii” Personalized treatment plans are important for people with alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS cell and tissue engineering”
2 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS cell and tissue engineering” Mesenchymal stem cells show promise for treating various skin conditions and may help regenerate hair.

A 32-year-old man with early graying hair shows a unique pattern, suggesting more research is needed on why hair grays early.
 May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
May 2024 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Low HDL-C, uric acid, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D are risk factors for early-onset male hair loss.
 1 citations,
August 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports”
1 citations,
August 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports” A woman's complete hair loss condition improved after recovering from COVID-19.
 30 citations,
December 2001 in “Experimental dermatology”
30 citations,
December 2001 in “Experimental dermatology” Gonadal hormones significantly affect the severity of alopecia areata in mice.





























