3 citations,
October 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Alopecia areata is a hair loss disease caused by complex immune reactions, and new targeted treatments show promise.
[object Object]  2 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
2 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Higher CRBP1 levels are linked to more severe alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
 January 2025 in “SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine”
January 2025 in “SKIN The Journal of Cutaneous Medicine” Baricitinib treatment for severe alopecia areata shows significant improvement by 52 weeks, especially in very severe cases.
 June 2024 in “Zagazig University Medical Journal”
June 2024 in “Zagazig University Medical Journal” Intralesional vitamin D is mildly effective for treating Alopecia Areata.
 June 2024 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
June 2024 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” PRP therapy effectively treats alopecia areata and atrophic acne scars.
 December 2023 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
December 2023 in “International journal of research in dermatology” Adding PRP to topical mometasone improves and speeds up alopecia areata treatment.
 November 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
November 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Combining calcipotriol and PRP is most effective for treating Alopecia Areata.
 April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Phototherapy helps some patients with alopecia areata regrow hair, especially those with hair at treatment start and less severe forms of the condition.
Microneedling with Triamcinolone acetonide is an effective, less invasive, and safe alternative to direct injections for treating alopecia areata.
 May 2022 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
May 2022 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Higher levels of PD-L1 are linked to more severe hair loss in people with Alopecia Areata.
April 2022 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Intralesional triamcinolone acetonide is more effective but has a higher relapse rate than platelet-rich plasma for treating alopecia areata.
January 2016 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” Hair UpTM effectively and safely promotes hair regrowth, especially in minors.
 September 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
September 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Microneedling mildly regrows hair in androgenetic alopecia but not in other types.

New treatments for skin conditions show promise, especially Coacillium® for hair growth in young people with alopecia areata.
 November 2023 in “Annales de dermatologie et de vénéréologie, FMC”
November 2023 in “Annales de dermatologie et de vénéréologie, FMC” Baricitinib effectively treats severe alopecia for up to 104 weeks.
 April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Machine learning can predict how well patients with alopecia areata will respond to certain treatments.
 September 2022 in “Intisasi sains media”
September 2022 in “Intisasi sains media” A young child with complete hair loss improved significantly with a combination of hair growth treatments and laser therapy.
 1 citations,
February 2024 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
1 citations,
February 2024 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Baricitinib effectively promotes long-term hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients.
 9 citations,
December 2012 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
December 2012 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Wearing wigs or hairpieces improves self-esteem, adaptability, and competence in women with alopecia areata.
 April 2024 in “Dermatology and therapy”
April 2024 in “Dermatology and therapy” There are significant gaps and inconsistencies in diagnosing and treating alopecia areata in Greece and Italy.
 5 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
5 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Lower vitamin D levels might be linked to more severe alopecia areata, but more research is needed to understand if vitamin D can help treat it.
 1 citations,
January 2024 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
1 citations,
January 2024 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Fractional CO2 laser with topical triamcinolone is more effective and safer for treating alopecia areata than intralesional triamcinolone.
 May 2022 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2022 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The document suggests using a topical Vitamin D treatment for hair loss rather than oral supplements and calls for more research.
22 citations,
September 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The study's results on the effectiveness of low-dose IL-2 for alopecia areata and its impact on immune cells were not provided.
[object Object]  April 2024 in “Skin research and technology”
April 2024 in “Skin research and technology” Minoxidil with triamcinolone acetonide is more effective for mild alopecia areata when injected with microneedles than when applied topically.
 63 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
63 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical JAK inhibitors may help treat some skin conditions but need more research.
 29 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
29 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology” People with alopecia areata often have lower vitamin D levels, which are linked to more severe and longer-lasting hair loss, but vitamin D receptor levels in the skin don't show the same pattern and don't predict treatment success.
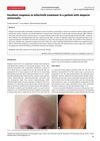 16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” A patient with complete hair loss regrew all her hair using tofacitinib.
 3 citations,
May 2019 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2019 in “International journal of research in dermatology” Platelet rich plasma is an effective treatment for alopecia areata.

























