59 citations
,
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science”
59 citations
,
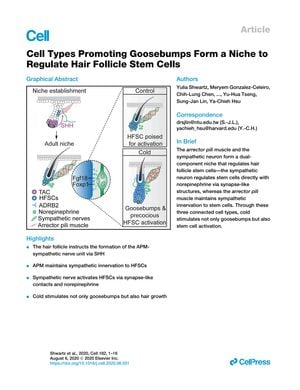
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science” Understanding how hair follicle stem cells work can help find new ways to prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.
260 citations
,
January 2020 in “Nature” Stress can cause hair to turn gray by depleting stem cells.
 61 citations
,
June 2018 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
61 citations
,
June 2018 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Light can turn on hair growth cells through a nerve path starting in the eyes.
 32 citations
,
July 2017 in “Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Developmental Biology”
32 citations
,
July 2017 in “Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Developmental Biology” Transit-amplifying cells are crucial for tissue repair and can contribute to cancer when they malfunction.
 106 citations
,
October 2016 in “Cell Stem Cell”
106 citations
,
October 2016 in “Cell Stem Cell” PDGFA/AKT signaling is important for the growth and maintenance of certain skin fat cells.
 75 citations
,
October 2016 in “Genes & Development”
75 citations
,
October 2016 in “Genes & Development” Cells in hair follicles help create fat cells in the skin by releasing a protein called Sonic Hedgehog.
142 citations
,
February 2016 in “Science” Foxc1 helps keep hair follicle stem cells inactive, preventing hair loss.
8 citations
,
January 2016 in “Cells tissues organs” Norepinephrine helps skin cells grow, which is important for hair growth.
173 citations
,
August 2015 in “Developmental cell” The study identified unique genes in hair follicle cells and their environment, suggesting these genes help organize cells for hair growth.
35 citations
,
December 2014 in “Lasers in surgery and medicine” Red light promotes hair growth by directly stimulating hair cells and improving cell communication.
 426 citations
,
August 2014 in “Nature Medicine”
426 citations
,
August 2014 in “Nature Medicine” Skin stem cells interacting with their environment is crucial for maintaining and regenerating skin and hair, and understanding this can help develop new treatments for skin and hair disorders.
 35 citations
,
March 2014 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
35 citations
,
March 2014 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in male pattern baldness involves muscle degeneration and increased scalp fat.
106 citations
,
February 2014 in “eLife” Lanceolate complexes in mouse hair follicles are essential for touch and depend on specific cells for maintenance and regeneration.
1235 citations
,
December 2013 in “Nature” Two fibroblast types shape skin structure and repair differently.
394 citations
,
October 2013 in “Nature”  22 citations
,
July 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
22 citations
,
July 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Miniaturized hairs stay connected to muscle in alopecia areata, allowing possible regrowth, but not in androgenetic alopecia.
 138 citations
,
June 2012 in “Genes & Development”
138 citations
,
June 2012 in “Genes & Development” Sonic hedgehog signaling is crucial for hair growth and maintaining hair follicle identity.
158 citations
,
February 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” FGF18 helps keep hair in its resting phase, affecting hair growth cycles.
 191 citations
,
September 2011 in “Cell stem cell”
191 citations
,
September 2011 in “Cell stem cell” Hair follicle stem cells use specific chromatin changes to control their growth and differentiation.
 396 citations
,
May 2011 in “Cell stem cell”
396 citations
,
May 2011 in “Cell stem cell” Nerve signals are crucial for hair follicle stem cells to become skin stem cells and help in wound healing.
294 citations
,
February 2011 in “Cell” Nephronectin helps attach muscle cells to hair follicles.
 479 citations
,
January 2005 in “BioEssays”
479 citations
,
January 2005 in “BioEssays” Hair follicle development is controlled by interactions between skin tissues and specific molecular signals.
949 citations
,
January 2001 in “Cell” Adult mouse skin contains stem cells that can create new hair, skin, and oil glands.
 22 citations
,
August 1999 in “Experimental Dermatology”
22 citations
,
August 1999 in “Experimental Dermatology” Certain drugs can cause early hair growth in mice by affecting the nerves.
17 citations
,
May 1995 in “Anatomy and Embryology” Injecting 6-OHDA in newborn mice delays hair growth and thins skin.