mometasone furoate
🛒 Where to find mometasone furoate
Tracking 4 topical products by companies like AllDayChemist and Amazon. View all 4 products »Research
20 / 247 results
research Bimatoprost Versus Mometasone Furoate in the Treatment of Scalp Alopecia Areata: A Pilot Study
Bimatoprost was found to be safer and more effective than mometasone furoate for treating scalp hair loss.

research Use of Adapalene in Alopecia Areata: Efficacy and Safety of Mometasone Furoate 0.1% Cream Versus Combination of Mometasone Furoate 0.1% Cream and Adapalene 0.1% Gel in Alopecia Areata
Combining mometasone furoate cream with adapalene gel is safer and more effective for hair regrowth in alopecia areata than using the cream alone.

research Topical Bimatoprost (0.03%) Versus Topical Mometasone Furoate (0.1%) in Treatment of Alopecia Areata
Mometasone furoate cream was more effective than bimatoprost solution for treating hair loss from Alopecia Areata.
research Efficacy and Safety of Combination of Mometasone Furoate 0.1% Cream and Adapalene 0.1% Gel in Alopecia Areata
The treatment is effective for mild alopecia areata but often causes mild side effects.
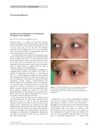
research Successful Use of Bimatoprost in the Treatment of Eyelash Alopecia
Bimatoprost helped a girl grow her eyelashes back quickly and without serious side effects.
research Amicrobial Pustulosis With Antinuclear Antibodies And Rheumatoid Factor
A woman with skin eruptions and hair loss improved significantly with ointment treatment.
research Alopecia Areata - Vitiligo Overlap Syndrome: An Emerging Clinical Variant
Alopecia areata and vitiligo can coexist, respond well to treatment, and may have a better prognosis together.

research Pressure Alopecia in Living Donors for Liver Transplantation
Pressure from surgical headrests can cause temporary hair loss in liver donors.

research The Use of Biodegradable Microneedle Patches to Increase Penetration of Topical Steroid for Prurigo Nodularis
Biodegradable microneedle patches help topical steroids work better for prurigo nodularis.
research Imatinib-Induced Classical Lichen Planopilaris in Blaschko-Linear Distribution Leading to Cicatricial Alopecia
Imatinib can cause hair loss due to lichen planopilaris.

research Dermoscopic Features of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
Dermoscopy is useful for diagnosing and monitoring discoid lupus erythematosus by showing specific skin patterns.

research Granuloma Annulare Mimicking Alopecia Mucinosa in a Child: An Atypical Presentation
Biopsy is crucial to correctly diagnose granuloma annulare, which can mimic other conditions like alopecia mucinosa.

research PA13: A Hair’s Breadth from Misdiagnosis
A 15-year-old boy was correctly diagnosed with a rare skin condition after initially being misdiagnosed.

research Follicular Psoriasis: A Case Report and Review of Literature
A man with follicular psoriasis got better after treatment with skin cream and allergy pills.
research An Unexplained Lesion on the Leg of a 2-Year-Old Girl
The girl's leg lesion was a fungal infection that improved with antifungal medication but kept coming back before finally clearing up after 5 years.

research Successful Combination Therapy of Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
The combination therapy effectively improved acne keloidalis nuchae.
research Erosive Pustular Dermatosis of Scalp: An Overlooked Entity
Recognizing erosive pustular dermatosis of the scalp is crucial to avoid misdiagnosis.
research Exacerbation of Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Following Vaccination with BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine
COVID-19 vaccines can trigger autoimmune flares but are still beneficial for patients with autoimmune conditions.

research Acne Necrotica in Its Entirety: When It Starts, and After It Evolves
Acne necrotica can be effectively treated with topical cream and antibiotics.

research Study of the Effect of Topical Mometasone with Intralesional Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Topical Mometasone Alone in the Treatment of Alopecia Areata
Adding PRP to topical mometasone improves and speeds up alopecia areata treatment.