63 citations,
April 2005 in “Mechanisms of development” Mice with too much Claudin-6 have skin barrier problems and abnormal hair growth.
 April 2024 in “Communications biology”
April 2024 in “Communications biology” Enzymes involved in Vitamin A metabolism affect hair growth and type in mice.
7 citations,
October 2019 in “Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology” Fusion proteins can protect hair from heat damage.
37 citations,
February 2010 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology” Androgen self-administration might be controlled by membrane receptors, not nuclear ones.
 1 citations,
August 2023 in “Gels”
1 citations,
August 2023 in “Gels” The hydrogel with silver and ibuprofen promotes wound healing and fights infection.
34 citations,
June 2005 in “Developmental dynamics” Runx3 helps determine hair shape.
1 citations,
December 2022 in “Plants” CSLD1 suppresses rice root hair growth with NH4+ and regulates AMT1;2 expression.
 98 citations,
February 2007 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology”
98 citations,
February 2007 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology” Androgens can both stimulate and cause hair loss, and understanding their effects is key to treating hair disorders.
 7 citations,
February 2016 in “Dermatology and therapy”
7 citations,
February 2016 in “Dermatology and therapy” t-Flavanone helps improve male pattern hair loss by making hair roots stronger.
 126 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
126 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that understanding hair structure is key to diagnosing hair abnormalities and recommends gentle hair care for management.
 122 citations,
May 2010 in “Plant Physiology”
122 citations,
May 2010 in “Plant Physiology” Different PIN proteins affect plant root hair growth by changing how auxin is transported.
 67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Hirsutism is excessive hair growth in women often caused by polycystic ovarian syndrome, and identifying the cause is important for managing associated health risks.
 66 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics”
66 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics” Androgens can both promote and prevent hair growth due to differences in gene expression in hair follicles.
 62 citations,
July 1993 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
62 citations,
July 1993 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair growth is influenced by interactions between skin layers, growth factors, and hormones, but the exact mechanisms are not fully understood.
 47 citations,
August 2000 in “Endocrine Reviews”
47 citations,
August 2000 in “Endocrine Reviews” The document concludes that more research is needed to understand excessive hair growth in women with normal hormone levels and regular ovulation.
 41 citations,
November 2013 in “Experimental Dermatology”
41 citations,
November 2013 in “Experimental Dermatology” Leptin, a hormone, is important for starting hair growth.
 30 citations,
January 2000 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
30 citations,
January 2000 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Finasteride and minoxidil are effective FDA-approved treatments for androgenetic alopecia.
 29 citations,
December 1998 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
29 citations,
December 1998 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” New treatments for hair loss show promise, especially finasteride for men and a stronger minoxidil formula.
 25 citations,
April 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
25 citations,
April 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” GasderminA3 is important for normal hair cycle transitions by controlling Wnt signaling.
 24 citations,
October 2019 in “Biomaterials Research”
24 citations,
October 2019 in “Biomaterials Research” Minoxidil in HA-PLGA nanoparticles effectively treats alopecia through skin delivery.
 24 citations,
November 1978 in “Biochemistry”
24 citations,
November 1978 in “Biochemistry” α-type filaments in guinea pig hair follicles have unique structural features.
 22 citations,
March 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
22 citations,
March 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Many treatments for hair loss lack proper testing and FDA approval, so their effectiveness is uncertain.
 18 citations,
January 1998 in “Endocrine”
18 citations,
January 1998 in “Endocrine” RU58841, a nonsteroidal anti-androgen, showed potential as a topical treatment for hair loss, increasing hair density, thickness, and length without systemic side effects in Stumptailed Macaques.
 13 citations,
March 2020 in “Genes”
13 citations,
March 2020 in “Genes” Disrupting the FGF5 gene in rabbits leads to longer hair by extending the hair growth phase.
 7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” T-cell reconstitution after thymus transplantation can cause hair whitening and loss.
 7 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
7 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Progranulin overexpression leads to shorter, thinner hair and increased cell death in mouse hair follicles.
 4 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
4 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Stress, nutritional issues, and chronic diseases can cause hair loss, and nail changes may signal internal diseases; treatment focuses on the underlying cause.
 3 citations,
January 2021 in “Wear”
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Wear” Hair's resistance to wear varies by ethnicity and treatment, with less wear indicating stronger hair.
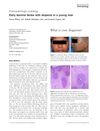 3 citations,
April 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
April 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A young man was diagnosed with trichoepitheliomas, causing thick skin and hair loss.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Melanocyte-associated antigens may play a key role in alopecia areata and could be targets for new treatments.
























