 33 citations,
April 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
33 citations,
April 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Psychological factors like depression may be more important than zinc, folate, and vitamin B12 levels in causing scalp pain in people with hair loss.
 33 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
33 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” A long-acting Vitamin C derivative helps hair grow by stimulating cells and increasing growth factors.
32 citations,
January 2006 in “Liver transplantation” Vitamin A toxicity can cause severe health issues and may require a liver transplant if other treatments fail.
[object Object] 28 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Low vitamin D can worsen pediatric alopecia areata.
 27 citations,
October 1945 in “Endocrinology”
27 citations,
October 1945 in “Endocrinology” Synthetic hormone treatment reduces melanin and hair growth in rats.
23 citations,
September 2016 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Vitamin D levels do not affect the risk of developing alopecia areata.
21 citations,
March 2014 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Targeting the Wnt pathway might help treat hair loss.
21 citations,
January 2009 in “Indian journal of dermatology, venereology, and leprology” Vitamin B12, folate, ferritin, and iron levels are not linked to alopecia areata.
20 citations,
June 2020 in “Journal of Advanced Research” High-dose vitamin A and E with zinc improved blood sugar control and insulin function in diabetics, but may cause hair loss.
20 citations,
July 1990 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Taking cyproterone acetate and ethinyl oestradiol for hair loss can lower vitamin B12 levels in women.
20 citations,
February 1977 in “The anatomical record” Excess vitamin A changes skin and hair follicle development and affects polysaccharide distribution.
 19 citations,
December 2008 in “Medical Journal of Australia”
19 citations,
December 2008 in “Medical Journal of Australia” Baldness does not affect vitamin D levels in men.
 18 citations,
October 2014 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine”
18 citations,
October 2014 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine” Eating vitamin A affects hair growth and health by changing cell signals in mice.
18 citations,
October 1978 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Excess vitamin A causes lasting gland changes in mouse hair follicles.
 17 citations,
July 2015 in “Biomolecules and Biomedicine”
17 citations,
July 2015 in “Biomolecules and Biomedicine” High Nesfatin-1 and low Vitamin D may increase blood pressure and heart rate in women with PCOS.
17 citations,
December 1951 in “Experimental biology and medicine” Vitamin B12 and aureomycin can reverse or reduce cortisone's negative effects on body and hair growth in rats.
16 citations,
January 2017 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Low levels of vitamin B12 and ferritin are linked to early hair graying.
 16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
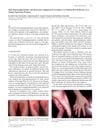
16 citations,
January 2008 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause skin darkening and increased blood vessels, but treatment can improve symptoms.
16 citations,
October 2007 in “PubMed” Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause skin darkening and white hair, but it's reversible.
 15 citations,
October 2016 in “PubMed”
15 citations,
October 2016 in “PubMed” People with Telogen Effluvium often lack vitamin D, ferritin, and zinc.
 15 citations,
May 2011 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
15 citations,
May 2011 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Vitamin A might be a safe extra treatment for dogs with sebaceous adenitis, but more research is needed to prove its effectiveness.
14 citations,
July 2022 in “Nutrients” Vitamin A is important for healthy skin and hair, influencing hair growth and skin healing, but UV light reduces its levels.
14 citations,
November 2021 in “Nanoscale” The research shows how a specially structured nanoemulsion delivers vitamins A and E through the skin.
 14 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
14 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Low vitamin D levels are linked to various types of hair loss, but more research is needed before using it as a treatment.
13 citations,
February 2020 in “CHEST Journal” Vitamin C supplementation can resolve pulmonary arterial hypertension caused by vitamin C deficiency.
13 citations,
May 2012 in “Cutaneous and ocular toxicology” Alopecia areata is not linked to vitamin B12 deficiency.
13 citations,
September 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Vitamin D receptor gene variations are not linked to alopecia areata.
[object Object] 12 citations,
September 2014 in “Bone” A vitamin D receptor mutation causes rickets and affects immune responses.
12 citations,
October 1952 in “Experimental biology and medicine” Vitamin B12 and aureomycin reduce the negative effects of high doses of cortisone in rats.
 10 citations,
January 2019 in “Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
10 citations,
January 2019 in “Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine” Certain variations in the vitamin D receptor gene are linked to an increased risk of polycystic ovary syndrome.










