 July 2020 in “International journal of biology sciences”
July 2020 in “International journal of biology sciences” Coconut oil mixed with egg yolk and vitamin E may improve rabbit hair growth more than other plant oils.
 March 2005 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2005 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Bexarotene 1% topical gel helped some patients with alopecia areata regrow hair.
January 2021 in “Asian Journal of Research in Dermatological Science” 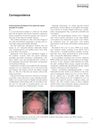 12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A woman developed a scalp condition from using minoxidil, which improved with a different treatment but left scarring.
 6 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of Dermatology”
6 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of Dermatology” Combination of 17α-estradiol and minoxidil improves hair growth and reduces hair loss in most patients.
3 citations,
October 2013 The new hydrogel and microemulsion could be better for hair loss treatment than current solutions.
1 citations,
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” HDAC inhibitors like Vorinostat and Entinostat may encourage hair regrowth and could be new treatments for hair loss conditions.
1 citations,
January 1998 in “International journal of cancer” Rubbing vitamin D3 on skin can help prevent hair loss from chemotherapy and slow breast tumor growth in mice.
April 2023 in “Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanoscience and Nanotechnology” The new formulation with minoxidil, chitosan, and Aloe vera improves hair growth and reduces side effects.
 81 citations,
August 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
81 citations,
August 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Latanoprost 0.1% may effectively treat hair loss.
21 citations,
April 2021 in “Biofabrication” The study created a skin model with realistic blood vessels that improves skin grafts and testing for drug delivery.
 17 citations,
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
17 citations,
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Fluridil safely promotes hair growth in men with androgenetic alopecia.
2 citations,
January 2010 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Dermatological drugs and cosmetics can cause serious side effects like cancer, allergies, and heart issues.
 August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The moisturizing cream used after a chemical peel was well tolerated and effectively moisturized the skin.
February 2023 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Minoxidil and PRP both help with hair growth, but Minoxidil has higher satisfaction and fewer side effects.
September 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”  August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Fluridil safely promotes hair growth in men with androgenetic alopecia.
 9 citations,
April 2021 in “Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy”
9 citations,
April 2021 in “Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy” Clascoterone is a new, effective, and safe acne treatment without systemic side effects.
 1 citations,
December 2015 in “The Egyptian Journal of Histology”
1 citations,
December 2015 in “The Egyptian Journal of Histology” Hypothyroidism harms rat skin, but topical triiodothyronine may help improve it.
 November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A new molecule was found to be a safe and effective skin lightener and anti-aging product.
 January 2021 in “Social Science Research Network”
January 2021 in “Social Science Research Network” The new treatment using tiny lipid carriers to deliver minoxidil and latanoprost directly to hair follicles shows promise for alopecia.
 August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A 5-year-old girl with a rare skin disorder was effectively treated with skin creams instead of oral medication.
August 2021 in “Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research” Plant extracts in shampoo improved hair thickness and density in men with hair loss.
October 2021 in “Technology transfer: innovative solutions in medicine” The combined treatment improved scalp health in women with early-stage hair loss.
 116 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
116 citations,
December 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Adult female acne treatment should be personalized, considering individual preferences and pregnancy, using various topical and oral medications while managing side effects and resistance.
 97 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
97 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The human hair follicle can store topical compounds and be targeted for drug delivery with minimal side effects.
 78 citations,
February 2011 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal”
78 citations,
February 2011 in “Canadian Medical Association Journal” Acne treatment varies, with topical and systemic therapies effective, and more research needed on treatment order and long-term effects.
64 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Topical oligonucleotide therapy targets hair follicles effectively.
11 citations,
January 2015 in “JOURNAL OF HEALTH SCIENCE” A 12-year-old boy's rare skin condition improved with topical treatments and may resolve by puberty.















