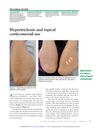
 February 2022 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine”
February 2022 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine” Prolonged use of topical corticosteroids can cause excessive hair growth.

Topical corticosteroid treatment showed no significant difference from placebo in treating alopecia areata in children.
 January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology”
January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology” Many treatments for alopecia areata have inconsistent results; for under 10s, use minoxidil with a corticosteroid, and for over 10s, add ILC and consider diphenylcyclopropenone for widespread cases.
[object Object]  16 citations,
January 2007 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
16 citations,
January 2007 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A man had an allergic reaction to minoxidil, which stopped after he discontinued use and started corticosteroids.
 6 citations,
February 2003 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
6 citations,
February 2003 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Topical corticosteroid was not more effective than placebo for children's alopecia areata, and atopy did not change treatment results.
 3 citations,
January 2018
3 citations,
January 2018 A woman had an unusual allergic reaction to a hair loss treatment, which cleared up after stopping the treatment and using a different medication.
 14 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
14 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A 9-year-old girl with alopecia areata had successful hair regrowth using bimatoprost after other treatments failed.
 5 citations,
February 2021 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
5 citations,
February 2021 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Platelet-rich plasma mesotherapy improved symptoms in patients with corticosteroid-induced rosacea-like dermatitis.
 10 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
10 citations,
April 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” Calcipotriol works almost as well as clobetasol for mild to moderate alopecia areata with fewer side effects.
New treatments for skin diseases in 1979 showed promising results with fewer side effects.
25 citations,
January 1978 in “JAMA” Topical corticosteroids can cause serious side effects like Cushing's syndrome and hirsutism.
 2 citations,
December 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
2 citations,
December 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” An elderly man's non-healing scalp lesion was successfully treated with a strong topical steroid.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Long-term Imiquimod treatment causes initial skin inflammation that lessens over time, and topical corticosteroids reduce this inflammation and cytokines in a mouse model of psoriasis.
74 citations,
April 2017 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Researchers found three patterns of Frontal fibrosing alopecia, with Pattern III having the best prognosis after treatment.
 47 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
47 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Most treatments for lichen planopilaris were found to be generally unsatisfactory.
 12 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
12 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A man with HIV developed skin and hair issues after starting HIV treatment, which improved with topical treatment.
9 citations,
September 2020 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” A woman developed vitiligo from repeated eyebrow microblading.
6 citations,
January 2014 in “Pediatric annals” A 21-day-old baby had a skin rash that didn't improve with cream and wasn't caused by a fungus.
 September 2022 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
September 2022 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Dermoscopy helped diagnose a rare skin disease which slightly improved with treatment.
 August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Experts recommend personalized treatment plans for best outcomes in managing Alopecia Areata.
10 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology” Mesalazine may help treat extensive alopecia areata effectively.
December 2018 in “International journal of women’s dermatology” Early diagnosis and strong corticosteroids are crucial for managing lymphocytic cicatricial alopecia.
21 citations,
May 2017 in “Paediatric drugs” Individualized treatment plans are crucial for children with alopecia areata, with promising options like JAK inhibitors showing significant hair regrowth.
 January 2019 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2019 in “International Journal of Trichology” A woman lost all her hair in one day, was diagnosed with a rare type of hair loss, and regrew it in 12 weeks with treatment.
 11 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
11 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Alopecia areata is a chronic condition causing hair loss, with new treatments targeting the immune system showing promise.
[object Object]  8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The review suggests there's no agreed treatment for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, but hydroxychloroquine and 5a-reductase inhibitors are most effective. New treatments like platelet-rich plasma and LED light could help if standard treatments fail.
 35 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
35 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Intralesional triamcinolone acetonide is effective for treating patchy hair loss, and dermoscopy helps detect treatment response and side effects early.
 13 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
13 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Certain factors like allergies, nail problems, and hair loss patterns can predict how well someone with patchy hair loss will respond to skin cream treatments.
 13 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
13 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Clobetasol and pimecrolimus are similarly effective for alopecia areata, but pimecrolimus has fewer side effects and is preferred for long-term use.
 12 citations,
January 2008 in “Drugs”
12 citations,
January 2008 in “Drugs” Some topical treatments like corticosteroids and vitamin D analogues are effective for scalp psoriasis, but more long-term data is needed.






















