 3 citations,
January 2021 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research”
3 citations,
January 2021 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research” Hair loss reduces hair thickness and coverage, but drug treatments mainly revive dormant hairs rather than reverse thinning; patients often undervalue their hair loss severity.
 78 citations,
September 2008 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
78 citations,
September 2008 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” The document concludes that various clinical methods are used to assess ageing skin and the effectiveness of anti-ageing products.
 1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks” Any drug can cause skin reactions, but antibiotics, NSAIDs, and psychotropic drugs are more common, with some reactions being life-threatening.
 1 citations,
February 2024 in “npj digital medicine”
1 citations,
February 2024 in “npj digital medicine” Researchers improved a skin disease diagnosis model using online images, achieving up to 49.64% accuracy.
 60 citations,
June 2019 in “Ageing Research Reviews”
60 citations,
June 2019 in “Ageing Research Reviews” Fat from the body can help improve hair growth and scars when used in skin treatments.
 17 citations,
December 2019 in “Stem Cells International”
17 citations,
December 2019 in “Stem Cells International” Bioactive molecules show promise for improving skin repair and regeneration by overcoming current challenges with further research.
 306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The skin has a complex immune system that is essential for protection and healing, requiring more research for better wound treatment.
 4 citations,
June 2022 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
4 citations,
June 2022 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” The new SFS Scale predicts hair transplant difficulty using hair and skin types, with thick skin and coily hair being hardest to work with.
 October 2023 in “Biomedical science and engineering”
October 2023 in “Biomedical science and engineering” Innovative methods are reducing animal testing and improving biomedical research.

Elastin-like recombinamers show promise for better wound healing and skin regeneration.
 40 citations,
January 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
40 citations,
January 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” The skin is the largest organ, protecting the body, regulating temperature, and producing hormones.
 87 citations,
December 2016 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
87 citations,
December 2016 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors may develop alopecia, but some hair regrowth is possible with treatment.
 162 citations,
July 2011 in “Biomacromolecules”
162 citations,
July 2011 in “Biomacromolecules” Chitosan nanofiber scaffolds improve skin healing and are promising for wound treatment.
 July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” The document concludes that understanding hair follicle histology and the hair cycle is crucial for diagnosing alopecia.
 140 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Controlled Release”
140 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Controlled Release” Microneedles improve drug delivery in various body parts, are safe and painless, and show promise in cosmetology, vaccination, insulin delivery, and other medical applications.
 1 citations,
June 2023 in “Cells”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “Cells” Exosomes could be a promising way to help repair skin and treat skin disorders.
 17 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of experimental zoology. Part B, Molecular and developmental evolution”
17 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of experimental zoology. Part B, Molecular and developmental evolution” Hair in mammals likely evolved from glandular structures, not scales.
 27 citations,
January 2010 in “Animal”
27 citations,
January 2010 in “Animal” South American camelids should be sheared early, fleece type affects fiber quality, and the S/P follicle ratio doesn't distinguish between Bolivian llama genotypes.
 3 citations,
April 2016 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration”
3 citations,
April 2016 in “Wound Repair and Regeneration” Researchers successfully transplanted hair follicles in mice, which survived well and helped in wound healing.
 155 citations,
May 2016 in “Nature communications”
155 citations,
May 2016 in “Nature communications” Memory T cells in the skin balance staying put and moving into the blood, clustering around hair follicles, and increasing in number after infection.
 20 citations,
June 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
20 citations,
June 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Using stem cells from fat tissue can significantly improve wound healing in dogs.
 116 citations,
August 2010 in “Nature”
116 citations,
August 2010 in “Nature” Scientists turned rat thymus cells into stem cells that can help repair skin and hair.
 October 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
October 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” The vitreous membrane in hair follicles changes shape during the hair cycle and may affect hair growth and nutrient exchange.
 68 citations,
September 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
68 citations,
September 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Shrinking skin cancer increases the chance of cancer in nearby lymph nodes.
 120 citations,
August 2008 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
120 citations,
August 2008 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Cytokeratin 19 and cytokeratin 15 are key markers for monitoring the quality and self-renewing potential of engineered skin.
1 citations,
November 2023 in “Polymers” Polyurethane dressings show promise for wound healing but need improvements to adapt better to the healing process.
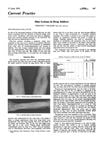 56 citations,
June 1970 in “The BMJ”
56 citations,
June 1970 in “The BMJ” Drug addicts often have scars, skin color changes, blocked veins, and bruising, with severe ulcers from barbiturate injections.
124 citations,
July 2017 in “eLife” Type XVII collagen helps control skin cell growth and could be a target for anti-aging treatments.
 21 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
21 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Rats can't grow new hair follicles after skin wounds, unlike mice, due to differences in gene expression and response to WNT signaling.
 82 citations,
March 2012 in “Development”
82 citations,
March 2012 in “Development” Drosha and Dicer are essential for hair follicle health and preventing DNA damage in skin cells.



























