 421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss with no cure and treatments that often don't work well.
1 citations,
January 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” The research identifies genes linked to wool quality in sheep and provides insights to improve wool production.
 June 2023 in “Buletin de psihiatrie integrativă”
June 2023 in “Buletin de psihiatrie integrativă” Alopecia causes significant emotional distress and psychological issues, requiring combined skin and mental health treatment.
 May 2023 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Thyroid disease can cause skin, hair, and nail problems, and treating the thyroid condition often improves these symptoms.
 20 citations,
January 2013 in “Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine”
20 citations,
January 2013 in “Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine” TGPC plus CGT is effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata in children.
 19 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
19 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Alopecia patients struggle with emotions and stress, and improving emotional intelligence may help manage hair loss.
 81 citations,
July 2011 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
81 citations,
July 2011 in “Lasers in Medical Science” The Lexington LaserComb helped regrow hair in mice with a condition similar to human hair loss.
 40 citations,
July 2017 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
40 citations,
July 2017 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Early and personalized treatment for hair loss in young people is crucial to prevent permanent damage and should include psychological support.
 9 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
9 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Scientists have found specific genes linked to different hair loss conditions, which could lead to new treatments.
 1 citations,
February 2024 in “International Journal of Pharmacognosy & Chinese Medicine”
1 citations,
February 2024 in “International Journal of Pharmacognosy & Chinese Medicine” Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Linn. has many medicinal benefits and needs proper identification for effective use.
 June 2011 in “CRC Press eBooks”
June 2011 in “CRC Press eBooks” Low-Level Laser Therapy can stimulate healing and cell function, potentially leading to wider medical use.
 19 citations,
May 2019 in “JAMA dermatology”
19 citations,
May 2019 in “JAMA dermatology” People with alopecia areata have similar overall death rates as others but higher risks of death from self-harm, psychiatric issues, and lung cancer in certain cases.
43 citations,
March 2010 in “Endocrine” 14 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Inflammation Research” Alopecia areata patients, especially women with nail issues or atopic diseases, are at higher risk for other autoimmune diseases.
6 citations,
October 2021 in “Biomedical Research and Therapy” Alopecia areata patients have higher levels of IL-6 and TNF-α.
15 citations,
March 2018 in “Cancer Medicine” Alopecia areata patients have varied cancer risks, with some cancers being lower and others higher.
 7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that various childhood hair and nail disorders exist, some may improve on their own, and advances in genetics and immunology could enhance treatment and counseling.
 1 citations,
October 2021 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2021 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” Alopecia areata mainly affects men aged 21-40 and is linked to autoimmune issues, thyroid problems, and inflammation.
 41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design”
41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design” Current and future treatments for alopecia areata focus on immunosuppression, immunomodulation, and protecting hair follicles.
 2 citations,
December 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
2 citations,
December 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are key for pediatric hair loss disorders, and addressing the emotional effects on children is important.
 3 citations,
July 2017 in “International journal of medicine”
3 citations,
July 2017 in “International journal of medicine” Intralesional triamcinolone acetonide effectively treats alopecia areata, as shown by significant improvements in hair regrowth and dermoscopic indicators.
 23 citations,
October 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
23 citations,
October 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Two transplant patients on cyclosporine unexpectedly developed hair loss.
 37 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in pharmacology”
37 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in pharmacology” Oral JAK inhibitors are effective and safe for treating alopecia areata but may need ongoing use to keep results.
13 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Simvastatin/ezetimibe may help some patients with severe alopecia areata regrow hair.
15 citations,
June 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Mice with extra human KLK14 had hair and skin problems, including weaker cell bonds and inflammation, linked to Netherton syndrome.
 18 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
18 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” High and low doses of prednisolone helped 62% of children with severe alopecia regrow hair with some weight gain and mild acne as side effects.
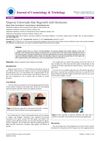 January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” A man with severe hair loss regrew hair after hormone treatment.
 3 citations,
November 2016 in “Clinical Pediatrics”
3 citations,
November 2016 in “Clinical Pediatrics” A girl with Crohn's disease developed hair loss from her medication, which improved with treatment but later returned.
 1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)”
1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)” The analysis aims to identify the most effective and safest treatments for alopecia areata.
 5 citations,
January 2009
5 citations,
January 2009 Betamethasone is more effective than Tacrolimus and soft paraffin for hair regrowth in patchy alopecia areata.























