 3 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
3 citations,
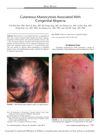
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” A 3-year-old girl with skin mast cell buildup and congenital baldness improved with treatment, suggesting a rare link between these conditions.
 14 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders”
14 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders” Misdiagnosis of LPP in AGA patients can cause hair transplant issues.
 July 2023 in “Biomolecules”
July 2023 in “Biomolecules” The new "whisker follicle microinjection assay" can test how different biomolecules affect hair growth and color.
14 citations,
January 2015 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Corticosteroid pulse therapy is more effective for severe alopecia areata than combination therapy.
 23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” The study concluded that AAI and DAA are forms of the same disease, with different symptoms in men and women, and that corticosteroid treatment is effective.
 27 citations,
September 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders”
27 citations,
September 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hair transplantation may work for some types of scarring alopecia, but results vary and more research is needed.
 13 citations,
March 2014 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
13 citations,
March 2014 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Minoxidil 5% solution significantly improved hair density in a girl with loose anagen hair syndrome over 28 months, with no side effects.
 March 2019 in “Applied sciences”
March 2019 in “Applied sciences” Laser therapy might help regrow hair in alopecia totalis better than steroids alone.
 1 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
1 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Platelet-rich plasma can increase hair density and may help treat some skin conditions, but it's costly, not FDA-approved, and needs more research.
 62 citations,
October 2016 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
62 citations,
October 2016 in “Dermatologic Therapy” PRP more effective than minoxidil 5% for treating alopecia areata.
 43 citations,
November 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
43 citations,
November 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair and nail changes can indicate health issues, including cancer and side effects from cancer treatments.
 1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
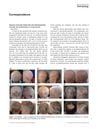
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl with alopecia universalis regrew most of her hair after treatment with simvastatin/ezetimibe, minoxidil, and prednisolone.
 September 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
September 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Raman spectroscopy is promising for measuring and enhancing drug delivery in alopecia treatments.
4 citations,
October 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” IL-4 and IL-13 might play a role in a type of hair loss similar to alopecia areata.
 9 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
9 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” People with pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus often have smaller sebaceous glands on their scalp.
 14 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
14 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A 9-year-old girl with alopecia areata had successful hair regrowth using bimatoprost after other treatments failed.
 2 citations,
December 2022 in “PNAS nexus”
2 citations,
December 2022 in “PNAS nexus” SCD-153 shows promise as an effective topical treatment for alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)”
1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)” The analysis aims to identify the most effective and safest treatments for alopecia areata.
9 citations,
January 2019 in “International Journal of Trichology” Combining calcipotriol with mometasone is more effective for treating alopecia areata than using mometasone alone.
 June 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
June 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Both DPCP alone and with PRP are effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.

Alopecia areata patients show increased inflammation and OX40 activation, suggesting a new treatment target.
 3 citations,
January 2018 in “Dermatology”
3 citations,
January 2018 in “Dermatology” Scalp biopsies help tell apart androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata.
 23 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
23 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Apremilast did not work for treating severe alopecia areata.
 176 citations,
August 2015 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
176 citations,
August 2015 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Alopecia areata involves immune activation in the scalp, suggesting treatments targeting TH1, TH2, and IL-23 pathways.
275 citations,
November 2002 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata mainly affects young people and has significant psychological impacts, especially in males.
 4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Various treatments exist for alopecia areata, but none are completely satisfactory; choice depends on age, disease extent, and preference.
January 2024 in “Biomedicines” The review shows that skin symptoms like chronic fungal infections, hair loss, and skin depigmentation are key for early detection and management of APECED.
 12 citations,
June 2023 in “JAMA network open”
12 citations,
June 2023 in “JAMA network open” JAK inhibitors effectively improve hair regrowth in alopecia areata with an acceptable safety profile.
 222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight”
222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight” Tofacitinib is safe and effective for severe alopecia areata, but hair loss may return 2 months after stopping treatment.
 21 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
21 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology” An 8-year-old girl with vitiligo developed extra hair growth on her knee after using tacrolimus ointment.

























