 13 citations,
September 2011 in “Archives of dermatology”
13 citations,
September 2011 in “Archives of dermatology” A patient with steroid sulfatase deficiency had a unique hair pattern and a brain malformation not previously linked to the condition.
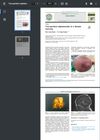 March 2023 in “Pediatrics & neonatology”
March 2023 in “Pediatrics & neonatology” A baby girl had two brain-related growths removed and is developing normally.
[object Object]  1 citations,
June 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
1 citations,
June 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Covers common skin issues in kids, their diagnosis, treatment, and need for specialist care.
 31 citations,
September 2013 in “Stem Cells”
31 citations,
September 2013 in “Stem Cells” Smad1 and Smad5 are essential for hair follicle development and stem cell sleepiness.
 192 citations,
March 2017 in “Cell host & microbe”
192 citations,
March 2017 in “Cell host & microbe” Hair follicle development and microbes help regulatory T cells gather in newborn skin.
 September 2018 in “Fertility and Sterility”
September 2018 in “Fertility and Sterility” High levels of testosterone and anti-Müllerian hormone before pregnancy are linked to a higher risk of newborns needing intensive care.
Type XVII collagen may help prevent skin aging.
 May 2023 in “Stem cell research & therapy”
May 2023 in “Stem cell research & therapy” New method efficiently isolates hair growth cells from newborn mouse skin.
 February 2024 in “Brain research bulletin”
February 2024 in “Brain research bulletin” Blocking androgen activity in newborn rats affects body weight and appetite-related hormones differently in males and females.
 February 2024 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology”
February 2024 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology” Higher anxiety during pregnancy is linked to lower cortisol levels in newborns' hair.
 5 citations,
January 2022 in “PloS one”
5 citations,
January 2022 in “PloS one” Deleting the p63 gene in certain cells causes problems in thymus development and severe hair loss in mice.
Different types of sun exposure can damage skin cells and affect healing, with chronic exposure being more harmful, and certain immune cells help in the repair process.
 5 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of radiation research”
5 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of radiation research” Vesicles from irradiated mouse cheek skin help cells survive radiation.
 19 citations,
March 1998 in “Endocrinology”
19 citations,
March 1998 in “Endocrinology” Male rats have more somatostatin neurons than females due to testosterone converting to estrogen during early development.
 48 citations,
March 2003 in “BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology”
48 citations,
March 2003 in “BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology” Mothers and newborns with dental fillings had higher mercury in their hair, but getting fillings during pregnancy didn't raise mercury levels further.
 3 citations,
March 2011 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
3 citations,
March 2011 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Acne in children varies by age and severity, requires a pediatric treatment approach, and may need diagnostic evaluation for underlying conditions.
 3 citations,
June 1997 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 1997 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Minoxidil treatment can stimulate hair growth in hairless puppies if applied early.
 July 2020 in “CRS 2020 Virtual Annual Meeting”
July 2020 in “CRS 2020 Virtual Annual Meeting” Researchers developed a new skin patch that delivers more finasteride into the skin, potentially improving treatment for hair loss and prostate issues.
January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Two newborns with rare skin infections were successfully treated with antifungal cream.
[object Object] October 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The conference concluded with plans for joint research into children's skin conditions and emphasized the importance of collaboration and patient-focused research.
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research” Constant light exposure during pregnancy changes newborn rabbits' skin, affecting hair follicles, skin thickness, and pigment cells.
 24 citations,
April 2012 in “Developmental Biology”
24 citations,
April 2012 in “Developmental Biology” Dermal papillae cells, important for hair growth, come from multiple cell lines and can be formed by skin cells, regardless of their origin or hair cycle phase. These cells rarely divide, but their ability to shape tissue may contribute to their efficiency in inducing hair growth.
124 citations,
July 2017 in “eLife” Type XVII collagen helps control skin cell growth and could be a target for anti-aging treatments.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The human skin's outer layer has more variety in cell types and development paths than previously thought.
 7 citations,
October 2015 in “American Journal of Primatology”
7 citations,
October 2015 in “American Journal of Primatology” Monkeys with hair loss during pregnancy showed higher stress hormone levels and invested differently in their offspring.
 14 citations,
August 2009 in “Cancer epidemiology”
14 citations,
August 2009 in “Cancer epidemiology” AHCC reduces hair loss and liver injury caused by chemotherapy in rodents.
 November 2022 in “Bioengineering”
November 2022 in “Bioengineering” The method can test hair growth products using a lab-made hair-like structure that responds to known treatments.
 January 2024 in “Biomaterials Research”
January 2024 in “Biomaterials Research” The new 3D system helps test hair growth treatments effectively.
 63 citations,
January 1992 in “Experimental Neurology”
63 citations,
January 1992 in “Experimental Neurology” Chickens exposed to loud noise can quickly regain hearing mostly due to repair of the tectorial membrane, not just hair cell regeneration.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Skin problems are common in Bangladesh due to arsenic, prompt treatment of diabetic foot ulcers is crucial, maternal transmission causes most neonatal herpes, treatments for pediatric vasculitis are effective, the chickenpox vaccine works, more frequent UVB therapy helps psoriasis, certain jobs increase hand dermatitis risk, monoclonal antibodies treat psoriasis well, lifestyle affects psoriasis, alefacept improves psoriasis, imiquimod cream partially clears basal cell carcinoma, and iron may not help chronic hair loss.























