January 2014 in “프로그램북(구 초록집)” Laser and light treatments show promise for hair growth but need more research.
15 citations,
January 2012 in “International journal of trichology” The HairCheck® device is effective for measuring hair loss and growth in people with alopecia.
 11 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
11 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” The conclusion is that treatments like finasteride and minoxidil can prevent baldness progression and improve hair density, but more research is needed on other therapies.
4 citations,
December 2020 Methotrexate may help stabilize frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 February 2024 in “Cosmoderma”
February 2024 in “Cosmoderma” Low-dose oral minoxidil can help treat male and female pattern hair loss, especially in those who can't use topical treatments or have heart health issues.
 October 2024 in “Small Methods”
October 2024 in “Small Methods” Platinum nanozyme microneedles can effectively and safely promote hair growth for androgenetic alopecia.
1 citations,
March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” Oral minoxidil may be a better treatment for hair loss than topical minoxidil.
 October 2024 in “World Journal of Psychiatry”
October 2024 in “World Journal of Psychiatry” Stress worsens hair loss in androgenetic alopecia.
 February 2022 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
February 2022 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” Topical minoxidil is the primary treatment for female pattern hair loss in India.
 43 citations,
May 1978 in “JAMA”
43 citations,
May 1978 in “JAMA” Minoxidil controls blood pressure but may cause kidney damage and needs diuretics to prevent swelling.
 40 citations,
September 2003 in “Archives of Dermatology”
40 citations,
September 2003 in “Archives of Dermatology” Finasteride slightly better long-term, minoxidil faster initial results, but stopping minoxidil may cause hair loss.
 23 citations,
June 1996 in “Toxicology”
23 citations,
June 1996 in “Toxicology” Older rats more affected by minoxidil's cardiotoxic effects than younger rats.
 14 citations,
September 2003 in “Archives of Dermatology”
14 citations,
September 2003 in “Archives of Dermatology” Finasteride may not stop severe hair loss after stopping minoxidil.
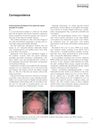 12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A woman developed a scalp condition from using minoxidil, which improved with a different treatment but left scarring.
 6 citations,
September 1988 in “Drug intelligence & clinical pharmacy”
6 citations,
September 1988 in “Drug intelligence & clinical pharmacy” Minoxidil caused a severe rash in a patient, which improved after stopping the drug.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Oral minoxidil can potentially increase hair growth in people suffering from Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia.
 May 2013 in “Reactions Weekly”
May 2013 in “Reactions Weekly” Using minoxidil can cause severe skin reactions in some people.
June 2022 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Oral minoxidil and growth factors improved hair density and thickness in a girl with hereditary hair loss.
 51 citations,
October 1980 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
51 citations,
October 1980 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Minoxidil lowers blood pressure effectively but may cause unwanted hair growth and other side effects.
 34 citations,
November 1987 in “Archives of Dermatology”
34 citations,
November 1987 in “Archives of Dermatology” Oral minoxidil helps hair regrowth in 80% of alopecia patients, but only 18% see cosmetic improvement.
 31 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
31 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Minoxidil helps stabilize hair loss, increase density, and reduce shedding after hair transplant surgery.
 17 citations,
June 2016 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
17 citations,
June 2016 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Treatment with dutasteride, minoxidil, and artificial hair transplantation improved appearance but caused folliculitis.
 12 citations,
January 2014 in “The Pan African medical journal”
12 citations,
January 2014 in “The Pan African medical journal” Minoxidil caused unwanted hair growth in a child, but stopped after stopping treatment.
 9 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
9 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A man lost a lot of scalp hair quickly after stopping minoxidil, but it grew back with mild male pattern baldness.
 2 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” Using 5% Minoxidil solution with oral chelated zinc supplement can effectively treat female pattern hair loss.

Minoxidil helps stimulate hair growth and enlarge small follicles in common hair loss, but doesn't stop it, and its effects can be boosted when combined with finasteride.
 January 2024 in “Vestnik oftalʹmologii”
January 2024 in “Vestnik oftalʹmologii” Stopping minoxidil and using prostaglandin analogues improved the man's eye condition.
 July 1987 in “Reactions (Auckland)”
July 1987 in “Reactions (Auckland)” Oral minoxidil may slow male pattern baldness and cause body hair growth, but hair loss can happen after stopping it.
Combining minoxidil with microneedling may be more effective for hair growth than using minoxidil alone.
January 2009 in “Journal of Pakistan Association of Dermatology” Systemic cyproterone acetate and 5% topical minoxidil are effective and safe for treating female pattern hair loss.






















