 13 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
13 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” Inflammation around hair follicles may worsen hair loss; evaluating and treating it can improve transplant results.
 105 citations,
December 2009 in “Archives of dermatology”
105 citations,
December 2009 in “Archives of dermatology” A specific drug can help treat Lichen Planopilaris, a condition causing permanent hair loss.
 129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopy can diagnose female hair loss with high accuracy by looking for specific patterns in hair and scalp appearance.
 32 citations,
July 2017 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
32 citations,
July 2017 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” New hair and skin changes were found in a rare case of syphilis-related hair loss.
 9 citations,
August 2014 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
August 2014 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Scalp areas that look normal in people with hair loss may still show signs of disease under a microscope.
 5 citations,
April 2016 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
5 citations,
April 2016 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” A tick bite caused temporary hair loss in a man, which is a rare condition that usually gets better within 3 months.
 5 citations,
May 2008 in “Nature Precedings”
5 citations,
May 2008 in “Nature Precedings” Trichoscopy is a useful non-invasive method to diagnose female hair loss with high accuracy.

COVID-19 can cause significant hair loss.
 1 citations,
October 2017 in “Our Dermatology Online”
1 citations,
October 2017 in “Our Dermatology Online” The conclusion is that a brown halo around hair follicles, seen in rapid hair loss, might be linked to inflammation or chemical exposure.
 March 2013 in “Hair transplant forum international”
March 2013 in “Hair transplant forum international” Inflammation linked to the immune response may play a role in causing various types of hair loss.
 33 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis”
33 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis” Alopecia Areata might be linked to Crohn's disease.
 36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy”
36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” No treatments fully cure or prevent alopecia areata; some help but have side effects or need more research.
 16 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
16 citations,
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Blocking interferon-gamma helps prevent and treat hair loss in Alopecia Areata.
 20 citations,
February 1985 in “Archives of Dermatology”
20 citations,
February 1985 in “Archives of Dermatology” Minoxidil helps hair regrowth, especially with more indeterminate hairs.
 10 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
10 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” More vellus hairs in frontal scalp indicate early female pattern hair loss.
 9 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of international medical research”
9 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of international medical research” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is linked to hypothyroidism but doesn't affect quality of life.
 9 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
9 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Most patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia are middle-aged women, often have thyroid disease, and some treatments can help stabilize the condition.
 8 citations,
March 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
8 citations,
March 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” The new hair loss treatment kit was safe and improved hair growth without any adverse effects.
 5 citations,
July 2019 in “Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy”
5 citations,
July 2019 in “Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy” Using tacalcitol ointment with photodynamic therapy may effectively treat follicular mucinosis with scalp hair loss.
 5 citations,
March 2012 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
5 citations,
March 2012 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” A woman experienced temporary hair loss after taking albendazole, which resolved on its own within 3 months.
 4 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
4 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” Accidental findings have led to new hair treatment discoveries, like using blood pressure and diabetes medications for hair loss and unwanted hair.
 3 citations,
September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
3 citations,
September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Avoiding allergens can improve skin and hair conditions in adults with allergic reactions.
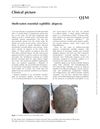 3 citations,
July 2014 in “QJM”
3 citations,
July 2014 in “QJM” A 35-year-old man had patchy hair loss that was actually due to syphilis, not alopecia areata.
 November 2023 in “European medical journal. Dermatology”
November 2023 in “European medical journal. Dermatology” Early diagnosis and new treatments are crucial to prevent permanent hair loss in scarring alopecia.
 July 2023 in “Dermatology Practical & Conceptual”
July 2023 in “Dermatology Practical & Conceptual” A positive anagen pull test can help detect active Lichen Planopilaris.
 January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology”
January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology” Many treatments for alopecia areata have inconsistent results; for under 10s, use minoxidil with a corticosteroid, and for over 10s, add ILC and consider diphenylcyclopropenone for widespread cases.
 June 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
June 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Title change to "Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia (CCCA)"; common in African American women; hair-grooming methods may contribute; no effective therapy found; trials needed.
 27 citations,
May 2007 in “Archives of dermatological research”
27 citations,
May 2007 in “Archives of dermatological research” Diphencyprone treatment increases CD8 lymphocytes in the scalp, which is associated with hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients.
 21 citations,
January 2013 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
21 citations,
January 2013 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” The combination of cyclosporine and PUVA might help treat severe alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
July 2014 in “Our Dermatology Online”
1 citations,
July 2014 in “Our Dermatology Online” The patient with both scarring and non-scarring hair loss showed complex immune reactions and improved with steroid treatment.





























