 7 citations,
September 2021 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia”
7 citations,
September 2021 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia” COVID-19 can cause temporary hair loss, often starting around 7-8 weeks after recovery, with factors like Vitamin D deficiency, other diseases, medication, and stress potentially contributing.
 4 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
4 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Monocytes might be linked to hair loss after COVID-19.
16 citations,
January 2017 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Low levels of vitamin B12 and ferritin are linked to early hair graying.
 3 citations,
April 2023 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
3 citations,
April 2023 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine” The study identified five types of long COVID symptoms and suggests tailored management strategies for each.
 February 2024 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas”
February 2024 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” Most alopecia areata patients in the study were women, aged 15-49, with patchy hair loss and often had other health conditions.
 May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia in men is genetic and linked to health issues like obesity and heart disease, with treatments including minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplants.
 30 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology”
30 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology” Birth control pills and cyproterone acetate can help treat acne in women, especially when linked to hormonal issues.
 16 citations,
June 2008 in “Springer eBooks”
16 citations,
June 2008 in “Springer eBooks” Over 50% of women over 50 experience hair loss, with minoxidil being the only proven effective treatment.
 March 2024 in “The journal of sexual medicine”
March 2024 in “The journal of sexual medicine” The therapies improved ejaculation disorders and sexual function in middle-aged men.
 129 citations,
November 2005 in “Internal Medicine Journal”
129 citations,
November 2005 in “Internal Medicine Journal” Early detection and intensive treatment of diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus toxins are crucial for reducing severe health effects.
 4 citations,
July 1994 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
4 citations,
July 1994 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome, linked to contaminated L-tryptophan supplements, caused severe symptoms and some deaths, with long-term effects in survivors.
 October 2021 in “Dermatology Reports”
October 2021 in “Dermatology Reports” Higher IL-17A levels indicate more severe alopecia areata.
 226 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
226 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Hair loss in women is genetic, diagnosed by examination and biopsy, and treated with minoxidil, finasteride, or transplantation.
 109 citations,
November 2004 in “Lupus”
109 citations,
November 2004 in “Lupus” The paper concludes that the 1982 criteria for diagnosing systemic lupus erythematosus need updating to improve accuracy and involve dermatologists in the process.
 88 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology”
88 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology” The document concludes that specific itchy skin diseases during pregnancy have varying fetal risks and treatments, including corticosteroids and other medications.
 84 citations,
November 2003 in “European journal of endocrinology”
84 citations,
November 2003 in “European journal of endocrinology” Women with androgenic alopecia are more likely to have polycystic ovaries and higher androgen levels, which may indicate PCOS.
 58 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
58 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Alopecia significantly lowers women's quality of life, with psychological and social challenges, highlighting the importance of early treatment and support.
 47 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
47 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Premature graying of hair may suggest health issues and currently lacks effective treatments.
 41 citations,
August 2007 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
41 citations,
August 2007 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Men with Kennedy disease have less chance of hair loss.
 39 citations,
January 2019 in “The World Journal of Men's Health”
39 citations,
January 2019 in “The World Journal of Men's Health” Testosterone replacement therapy can prevent men from fathering children and should not be used by those wanting to stay fertile.
 23 citations,
March 1994 in “Fertility and sterility”
23 citations,
March 1994 in “Fertility and sterility” Most patients improved with oral contraceptives, but some needed additional treatment.
 22 citations,
April 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
22 citations,
April 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” More research is needed to determine if iron deficiency causes hair loss.
 18 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
18 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Mesotherapy for hair loss can sometimes cause more hair loss and scarring.
 14 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
14 citations,
March 2014 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Young adults with hair loss face higher risk of stiff arteries.
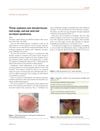 13 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
13 citations,
October 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that early recognition and appropriate treatment of red scalp, red ear, and red scrotum syndromes can lead to remission.
 11 citations,
November 2013 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
11 citations,
November 2013 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Azelaic Acid is effective and safe for treating adult female acne, with few side effects.
 6 citations,
January 2020 in “The Aging Male”
6 citations,
January 2020 in “The Aging Male” Testosterone replacement therapy improved blood sugar and fat levels without raising prostate cancer risk in Japanese men with low testosterone.
 5 citations,
January 1987 in “Gynecologic and obstetric investigation”
5 citations,
January 1987 in “Gynecologic and obstetric investigation” Cyproterone acetate implants were more effective at reducing facial hair and improving skin in severe hirsutism than oral treatment.
 4 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology Research and Therapy”
4 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology Research and Therapy” Anti-androgens are safe and effective for treating moderate to severe adult female acne.
 2 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
2 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Female pattern hair loss involves thinning hair on crown and frontal scalp, diagnosed by hair ratio, and treated with minoxidil, antiandrogens, or hair transplantation.




























