 1 citations,
June 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
June 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Activating β-catenin in mammary cells leads to changes that cause early-stage abnormal growths similar to skin structures.
 July 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
July 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The early genes of a specific virus can cause abnormal skin cell growth and hair follicle changes.
March 2022 in “Veterinary dermatology” A one-year-old cat had multiple benign skin tumors similar to those known in humans.
July 2021 in “Veterinary record/The veterinary record” A calf in Scotland likely had Schmallenberg virus from its mother.
 March 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
March 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Suppressing very long chain fatty acids is linked to skin cancer.
Toxins can disrupt skin stem cell balance, causing skin overgrowth or ulceration.
December 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Hedgehog signaling controls hair follicle development and can affect skin cancer growth.
22 citations,
July 2020 in “iScience” Sox21 is crucial for tooth development and enamel formation by preventing cells from changing into a different type.
 7 citations,
January 2016 in “Case reports in pediatrics”
7 citations,
January 2016 in “Case reports in pediatrics” A girl with Becker's nevus syndrome showed good improvement in breast development using spironolactone.
4 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of pediatric neurology” Becker's Nevus Syndrome is a rare condition with a skin patch and possible bone and muscle abnormalities, treated mainly for appearance.
1 citations,
June 2023 in “Medicina” People with Epidermolysis bullosa have many health problems including poor oral health, which is often neglected due to other medical issues.
 January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” The report concludes that atypical Brauer nevus is more common in males, present at birth, and often misdiagnosed due to its unusual scalp locations.
 November 2004 in “Medical Journal of Indonesia”
November 2004 in “Medical Journal of Indonesia” Hormonal imbalances can cause skin and hair problems in women, and treatments that block male hormones can help.
60 citations,
August 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The term "porokeratotic adnexal ostial nevus" is proposed to unify overlapping skin conditions involving eccrine and hair follicles.
 October 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
October 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Skin changes in Pseudoxanthoma elasticum patients can indicate the severity of related health issues.
149 citations,
January 2011 in “Nature reviews. Urology” Hormonal interactions, especially involving DHT and estrogen, play a key role in BPH development and treatment.
22 citations,
September 2014 in “JAMA dermatology” Ichthyosis with confetti is a genetic skin disorder with consistent ectodermal malformations and various KRT10 gene mutations.
4 citations,
April 2012 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Krt16-deficient mice help understand skin disorders like PC and FNEPPK.
467 citations,
May 1999 in “Molecular Cell” The study investigated the effects of activating the protooncogene c-Myc in adult skin epidermis. Researchers used a switchable form of c-Myc protein, c-MycER, to target the suprabasal epidermis. Activation of c-MycER led to rapid proliferation and disrupted differentiation of keratinocytes, resulting in papillomatosis and angiogenesis, which are similar to hyperplastic actinic keratosis, a precancerous condition. Importantly, these premalignant changes regressed spontaneously when c-MycER was deactivated, indicating that the effects were reversible.
 90 citations,
January 2003 in “The Journal of Urology”
90 citations,
January 2003 in “The Journal of Urology” Finasteride may reduce prostate bleeding by lowering blood vessel growth factor levels and blood vessel density in certain prostate areas.
33 citations,
March 1994 in “PubMed” The study investigated the expression patterns of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) and keratins in early papillomas in SENCAR mice to identify markers for early skin tumorigenesis. Tumors were induced using 7,12-dimethylbenzanthracene and promoted with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. In early papillomas, keratin K1 showed patchy staining, while K10 was minimally expressed, contrasting with their normal expression in mildly hyperplastic epidermis. ODC expression was intense and diffuse in suprabasal cells of papillomas, correlating with decreased K1 and K10 expression, indicating altered differentiation. These findings suggested that high ODC expression and reduced K1 and K10 could serve as markers for early tumorigenesis in mouse skin.
23 citations,
December 2008 in “Pediatric neurology” The document adds two cases of Gomez-Lopez-Hernandez syndrome and suggests including trigeminal anesthesia and scalp alopecia as key diagnostic criteria.
 19 citations,
August 2020 in “Gastroenterology report”
19 citations,
August 2020 in “Gastroenterology report” There is no standard treatment for the rare Cronkhite–Canada syndrome, which can be fatal and lead to cancer.
8 citations,
March 2010 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The 14-3-3σ gene is essential for preventing hair loss.
 1 citations,
September 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Aging reduces stem cell activation, leading to hair loss in mice lacking a specific enzyme.
1 citations,
January 1989 in “Carcinogenesis” The study investigated the effects of dexamethasone (DXME) on mouse skin treated with 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate (TPA). DXME, when applied after TPA, inhibited both the dermal inflammatory reaction and the induction of epidermal ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) activity. During the hyperplastic stage, DXME continued to counteract inflammation but only weakly inhibited ODC induction. Interestingly, in DXME-protected skin, the hyperplastic stage was delayed, and TPA strongly induced ODC activity in the epidermal cell layer before this stage. The study suggested that as the proliferation process was induced, epidermal cells became more sensitive to TPA, potentially becoming less reliant on inflammatory factors for ODC induction.
 March 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
March 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” The man was diagnosed with Cronkhite-Canada syndrome, a rare disorder with GI polyps, skin issues, hair loss, and nail problems.
 January 2023 in “International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics”
January 2023 in “International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics” A rare genetic disease causes rickets and often hair loss in young children, which can improve with specific treatments.
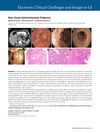 August 2013 in “Gastroenterology”
August 2013 in “Gastroenterology” A 60-year-old man with Cronkhite-Canada syndrome improved with treatment, but the condition has a high mortality rate and a risk of colorectal cancer.
 72 citations,
July 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
72 citations,
July 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Mice lacking a key DNA methylation enzyme in skin cells have a lower chance of activating stem cells necessary for hair growth, leading to progressive hair loss.














