Early treatment is important for better hair regrowth in elderly women with hair loss.
26 citations,
August 1995 in “The journal of experimental zoology/Journal of experimental zoology” Melatonin treatment made ferrets grow their fur earlier and affected their breeding time.
August 2006 in “Experimental dermatology” New treatments targeting insulin, blood flow, and inflammation could improve hormone-related hair conditions with fewer side effects.
 97 citations,
September 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders”
97 citations,
September 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders” The sebaceous gland has more roles than just producing sebum and contributing to acne, and new research could lead to better skin disease treatments.
 May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine”
May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine” Excessive hair growth in women, often from high androgen levels, is usually caused by PCOS, and can be treated with hair removal, medication, and possibly weight loss.
7 citations,
May 1977 in “Deutsche medizinische Wochenschrift/Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift” Antiandrogen treatments can help with various women's health issues but often require ongoing use.
 2 citations,
June 2020 in “AIDS”
2 citations,
June 2020 in “AIDS” Recreational drug use can cause misdiagnosed conditions and drug interactions in HIV patients.
 1 citations,
November 1998 in “Journal of Small Animal Practice”
1 citations,
November 1998 in “Journal of Small Animal Practice” The dog had a Sertoli cell tumor, which was successfully removed with surgery.
 43 citations,
July 1984 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
43 citations,
July 1984 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Antiandrogen therapy helped increase hair growth in women with hormonal imbalances related to baldness.
 130 citations,
September 1990 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
130 citations,
September 1990 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Flutamide effectively reduced excessive hair growth and improved related symptoms in hirsutism patients without significant side effects.
 12 citations,
February 2001 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy”
12 citations,
February 2001 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy” No effective treatment for hair loss after childbirth was found, but it usually gets better on its own and some cosmetic methods might help.
25 citations,
August 1989 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine” Birth control pills are effective for treating women with too much male hormone.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “International journal of women's health and reproduction sciences”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “International journal of women's health and reproduction sciences” Electroacupuncture improved symptoms of PCOS in a 19-year-old woman.
 15 citations,
January 2016 in “Przeglad Menopauzalny”
15 citations,
January 2016 in “Przeglad Menopauzalny” Eating a balanced diet with specific nutrients is important for menopausal women to manage hair loss.
9 citations,
December 1987 in “European journal of endocrinology” The treatment significantly reduced hair growth and male hormone levels in hirsute women.
 75 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism”
75 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in endocrinology and metabolism” Male hormones are important for hair and oil gland development and can cause conditions like excessive hair growth and acne.
 1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” Only minoxidil and finasteride are FDA-approved for hair loss, with other treatments available but less effective or with side effects.
 19 citations,
January 2013 in “Pediatrics in review”
19 citations,
January 2013 in “Pediatrics in review” The document says menstruation is important for women's health, discusses menstrual disorders, and suggests personalized treatment options.

Women with androgenetic alopecia have normal levels of most blood steroids and binding proteins, but higher dehydroepiandrosterone. Some also have low "sex hormone-binding globulin" and "corticosteroide-binding globulin" capacity, and high "free androgen index" and "free cortisol index". Diane treatment can normalize these levels and improve hair conditions.
14 citations,
January 1980 in “Journal of steroid biochemistry/Journal of Steroid Biochemistry” Both treatments reduced androgen levels and hair growth in women with hirsutism.
 8 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of Dermatology”
8 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of Dermatology” A topical treatment safely and effectively reduced acne by causing targeted cell death in sebaceous glands without side effects.
 17 citations,
January 2015 in “MedChemComm”
17 citations,
January 2015 in “MedChemComm” New treatments for prostate cancer are less toxic and show promise, but more research is needed to enhance their effectiveness and reduce side effects.
 November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Treatments for hair loss include hormone modifiers, minoxidil, and hair transplant surgery.
 8 citations,
March 2020 in “Metabolites”
8 citations,
March 2020 in “Metabolites” Finasteride treatment changes urine metabolomics and steroid signatures, potentially monitoring effectiveness but may cause sexual side effects.
 February 1960 in “Journal of the American Medical Association”
February 1960 in “Journal of the American Medical Association” Treatments for hair loss include estrogen therapy and special shampoos.

Resveratrol improved hormone levels, menstrual cycles, hair loss, and ovarian function in PCOS patients.
 2 citations,
March 2004 in “Reviews in Gynaecological Practice”
2 citations,
March 2004 in “Reviews in Gynaecological Practice” Hormonal changes and psychological issues can cause sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal women. Behavioral therapy is recommended first, with hormone replacement helping some symptoms but not libido. Testosterone can improve libido, but its effects on overall sexual function are unclear. Emotional and relationship issues should be addressed before using medication, and the benefits and risks of testosterone supplementation should be considered.
 26 citations,
January 2020 in “Przegląd Menopauzalny”
26 citations,
January 2020 in “Przegląd Menopauzalny” Menopausal women have higher androgen levels, which can cause symptoms like facial hair growth and low sexual desire.
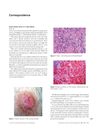 October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology” An 86-year-old man with prostate cancer was diagnosed with a rare, low-grade breast cancer and underwent surgery but declined additional hormone therapy.
 February 1976 in “PubMed”
February 1976 in “PubMed” Sex hormone therapy is effective for certain skin conditions like acne and seborrhea, but less so for female hair loss and excessive hair growth.
























