 65 citations,
August 2007 in “Experimental Dermatology”
65 citations,
August 2007 in “Experimental Dermatology” Human hair follicles can make and process prostaglandins, which may affect hair growth.
[object Object]  30 citations,
May 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
30 citations,
May 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Intermediate hair follicles are a better model for studying hair growth and testing hair loss treatments.
 22 citations,
June 2013 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
June 2013 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Early stage bald spots are linked to skin inflammation and damage to the upper part of the hair follicle.
1 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Lower proximal cup cells, not bulge stem cells, regenerate hair follicles after chemotherapy.
 1 citations,
July 2005 in “Drugs and the pharmaceutical sciences”
1 citations,
July 2005 in “Drugs and the pharmaceutical sciences” Targeting drugs to hair follicles can treat skin conditions, but reaching deep follicle areas is hard and needs more research.
 1 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
1 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” FGF18 treatment during hair's resting phase can protect against hair loss from radiation.
 December 2024 in “Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin”
December 2024 in “Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin” Gum arabic improves minoxidil delivery to hair follicles, enhancing hair growth.
 April 2021 in “Current Topics in Nutraceutical Research”
April 2021 in “Current Topics in Nutraceutical Research” Citron seed oil may help prevent or treat hair loss by promoting hair growth and increasing hair density.
 September 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
September 2014 in “Springer eBooks” Aging causes hair to gray and thin, with the timing of graying varying by race, and factors like oxidative stress and genetics can lead to hair loss.

Chrysanthemum zawadskii extract may help treat hair loss by promoting hair growth and affecting growth factors.
 19 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research”
19 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research” The main causes of diffuse hair loss in women are telogen effluvium and androgenetic alopecia, often related to stress and iron deficiency.
152 citations,
December 2003 in “Micron” As people age, their hair follicles produce less pigment, leading to gray and white hair, due to factors like reduced enzyme activity and damage to melanocyte DNA.
57 citations,
April 2009 in “Differentiation” SDF-1/CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 are crucial for melanocyte movement in mouse hair follicles.
 55 citations,
November 2018 in “American journal of human genetics”
55 citations,
November 2018 in “American journal of human genetics” Mutations in the LSS gene cause a rare type of hereditary hair loss.
 54 citations,
July 1967 in “Science”
54 citations,
July 1967 in “Science” Decomposed tritiated thymidine is less accurate for DNA tracing, and hair changes can indicate malnutrition.
 45 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
45 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Plasmacytoid dendritic cells are a key factor in causing hair loss in alopecia areata and could help differentiate it from other hair loss conditions.
[object Object]  41 citations,
March 2007 in “Journal of dermatological science”
41 citations,
March 2007 in “Journal of dermatological science” Taking L-cystine and vitamin B6 can prevent hair loss caused by smoke in mice.
 35 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
35 citations,
October 2015 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” Tiny particles carrying roxithromycin can effectively target and deliver the drug to hair follicles without irritation.
34 citations,
June 2005 in “Developmental dynamics” Runx3 helps determine hair shape.
 33 citations,
August 1973 in “American Heart Journal”
33 citations,
August 1973 in “American Heart Journal” Propranolol can cause reversible hair loss.
 28 citations,
January 2007 in “Dermatology”
28 citations,
January 2007 in “Dermatology” Chemotherapy can cause rapid, extensive hair loss, with patterns varying between individuals.
 23 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences”
23 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences” Finasteride cream helps hair growth with less side effects.
 20 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
20 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The protein ARA70/ELE1 is involved in male pattern baldness, and lower levels of its short form may lead to hair thinning.
 20 citations,
November 1968 in “The Lancet”
20 citations,
November 1968 in “The Lancet” Potassium levels affect blood sugar and insulin during dialysis, and malnutrition changes children's hair roots.
 15 citations,
April 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
15 citations,
April 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Botulinum toxin injections may help treat hair loss by blocking harmful secretion in hair follicles.
9 citations,
September 2013 in “Journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry/The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry” Matriptase is highly active in hair follicles and sebaceous glands, especially during hair growth phases.
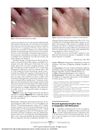 9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” Sunlight exposure improved a patient's skin condition, and there may be a link between a certain disease and skin growths; a leukemia treatment caused changes in hair color and growth.
8 citations,
March 2009 in “Differentiation” Adult vibrissa follicle stem cells can regenerate hair follicles, glands, and skin.
 7 citations,
December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The report suggests that hair loss in Cronkhite-Canada syndrome may be caused by alopecia areata incognita, as shown by a patient's improvement with treatment.
5 citations,
August 1981 in “Archives of Dermatology” Alopecia areata may be caused by the immune system attacking hair follicles.























