 17 citations,
November 2012 in “Maturitas”
17 citations,
November 2012 in “Maturitas” The conclusion is that proper evaluation and treatment of hair loss in midlife women is important, considering the emotional impact and potential for various treatments.
 July 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
July 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Hemp seed biomaterials may reduce hair loss and improve hair growth.
 8 citations,
November 2019 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
8 citations,
November 2019 in “Dermatologic Clinics” AGA treatments like minoxidil and LLLLT are safe and effective for gender minority patients.
 16 citations,
December 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
16 citations,
December 2006 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Hair follicles are essential for skin health, aiding in hair growth, wound healing, and immune function.
 28 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
28 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Genetics affect early female hair loss, severity depends on duration, and low ferritin levels not significant.
 34 citations,
November 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
34 citations,
November 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair extensions can cause hair loss and scalp damage, and these problems might be more common than people realize.
 February 2004 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
February 2004 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” The book is a comprehensive resource on hair disorders, but lacks information on some conditions.
 19 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
19 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Dermal papilla cells are key for hair growth and could help us understand and treat hair loss.
 6 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
6 citations,
November 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” Topical botanical lotion increases hair density and improves quality of life in women with hair loss.
 7 citations,
February 2022 in “Stem cell reviews and reports”
7 citations,
February 2022 in “Stem cell reviews and reports” Skin cells show flexibility in healing wounds and forming tumors, with potential for treating hair disorders and chronic ulcers.
 6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs”
6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs” Psychotropic drugs can cause hair loss or excessive hair growth.
 6 citations,
March 1999 in “Journal of pediatric health care”
6 citations,
March 1999 in “Journal of pediatric health care” The document emphasizes the need for primary care providers to understand and care for African American children's hair and skin to boost their self-esteem.
 97 citations,
March 2002 in “Molecular and cellular biology”
97 citations,
March 2002 in “Molecular and cellular biology” Mutant CDP/Cux protein causes hair defects and reduced male fertility in mice.
 86 citations,
October 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology”
86 citations,
October 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology” The Foxn1 gene mutation causes hairlessness and immune system issues, and understanding it could lead to hair growth disorder treatments.
 1 citations,
August 2023 in “Cutis”
1 citations,
August 2023 in “Cutis” Low ferritin levels can indicate iron deficiency as a cause of hair loss.
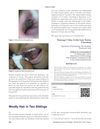 January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Two siblings have a rare genetic condition causing curly, coarse hair.
 6 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology”
6 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology” About 69% of school children in Kashmir valley have skin disorders, with eczema and acne being the most common.
 November 2024 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
November 2024 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Reduced alpha smooth muscle actin may cause hair loss in androgenetic alopecia.
 June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” The Middle East and Africa need better data, treatment consensus, and support for Alopecia Areata.
 8 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
8 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Minoxidil, finasteride, and low-level laser light therapy are effective FDA-approved treatments for hair loss.

Changes in skin bacteria can affect hair loss and new treatments targeting these bacteria may prevent balding without sexual side effects.
 66 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics”
66 citations,
January 2000 in “Hormone Research in Paediatrics” Androgens can both promote and prevent hair growth due to differences in gene expression in hair follicles.
 6 citations,
October 2014 in “PubMed”
6 citations,
October 2014 in “PubMed” Autoimmune diseases like lupus, dermatomyositis, and scleroderma can cause hair loss and other hair problems, and treatments for these diseases might also affect hair.
 139 citations,
July 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
139 citations,
July 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Understanding hair follicle anatomy helps diagnose hair disorders.

Androgenetic alopecia, or hair loss, is caused by a mix of genetics, hormones, and environment, where testosterone affects hair growth and causes hair to become smaller and grow for a shorter time.
 January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders” Laser treatment for hair loss works equally well on different skin types, but more research is needed for very dark skin.
 75 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
75 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Chronic Telogen Effluvium is a hair loss condition in middle-aged women that usually doesn't lead to complete baldness.
 47 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
47 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Hair diversity is influenced by complex genetics and environmental factors, requiring more research for practical solutions.
 6 citations,
June 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
6 citations,
June 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a poorly understood condition that is hard to treat and causes distressing hair loss.
 3 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
3 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document says that there are treatments for hair and nail diseases.






























