 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A new peptide, FOL-005, may help treat excessive hair growth by reducing a hair growth promoter, FGF7.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” 17β-estradiol may help hair growth by increasing cannabinoid receptor type 1.
 January 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
January 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Small molecule DMF improves psoriasis and multiple sclerosis, adult skin cells can be made to grow new hair, certain skin cells initiate hair growth, IL-17C controls gut health and can cause skin inflammation, and skin cells produce IL-17 that can lead to psoriasis.
 February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Mimicking growth factors in a topical solution can prolong hair growth phase and reduce hair loss without side effects.
 8 citations,
March 2019 in “Open Biology”
8 citations,
March 2019 in “Open Biology” The document concludes that regenerating functional ectodermal organs like teeth and hair is promising for future therapies.
 1 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a chronic skin condition best treated early with surgery for better outcomes and less recurrence.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Transplanting skin cells is a safe, effective, and affordable treatment for vitiligo.
 1 citations,
January 2010 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology”
1 citations,
January 2010 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that effective acne treatment requires a personalized combination of therapies and long-term commitment, with retinoids being important for maintenance.
 65 citations,
June 2003 in “EMBO journal”
65 citations,
June 2003 in “EMBO journal” Noggin overexpression delays eyelid opening by affecting cell death and skin cell development.
 63 citations,
October 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
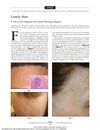
63 citations,
October 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Isolated long hairs at the original hairline can help diagnose Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia.
 48 citations,
May 2015 in “NPJ microgravity”
48 citations,
May 2015 in “NPJ microgravity” A 3-month stay in space causes skin thinning, disrupts hair growth, and changes muscle-related genes in mice.
 41 citations,
December 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Understanding how melanocyte stem cells work could lead to new treatments for hair graying and skin pigmentation disorders.
 17 citations,
May 1998 in “Contact Dermatitis”
17 citations,
May 1998 in “Contact Dermatitis” Minoxidil can cause pustular allergic reactions on skin.
 August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Too much β-catenin activity can mess up the development of mammary glands and make them more like hair follicles.
 October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” The gene Foxn1 is important for hair growth, and understanding it may lead to new alopecia treatments.
 97 citations,
September 2006 in “Pharmaceutical Research”
97 citations,
September 2006 in “Pharmaceutical Research” No treatment fully prevents hair loss from chemotherapy yet.
 40 citations,
March 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
40 citations,
March 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Growing hair follicles have high mitochondrial activity and ROS in specific regions, aiding hair formation.
 12 citations,
September 2020 in “Stem cell research & therapy”
12 citations,
September 2020 in “Stem cell research & therapy” Adult skin cell-based early-stage skin substitutes improve wound healing and hair growth in mice.
 11 citations,
July 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs”
11 citations,
July 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs” New hair loss treatments may include topical medications, injections, and improved transplant methods.
 4 citations,
August 2021 in “The Malaysian journal of medical sciences/The Malaysian Journal of Medical Science”
4 citations,
August 2021 in “The Malaysian journal of medical sciences/The Malaysian Journal of Medical Science” Eating fewer calories improves the ability of stem cells to repair and renew the body in various tissues.
11 citations,
May 2012 in “Genesis” Bmpr2 and Acvr2a receptors are crucial for hair retention and color.
1 citations,
January 2013 Glucosylceramides are essential for healthy skin and proper wound healing.
 November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Activating a bitter taste receptor in hair follicles can stop hair growth by increasing a specific growth factor.
 November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Butyrate helps hair grow longer, improves hair cell health, increases pigment production, and boosts hair's natural defenses.
33 citations,
March 2018 in “Trends in cell biology” Metabolism plays a key role in determining stem cell fate.
9 citations,
August 2021 in “Experimental dermatology” Hidradenitis suppurativa is a skin disease caused by the breakdown of the skin's natural immune barriers, especially around hair follicles.
 2 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Pathology of Nepal”
2 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Pathology of Nepal” Most skin cysts were common types found in unusual body parts, and examining tissue samples is important for accurate diagnosis.
March 2021 in “Cell stem cell” Skin cell behavior is influenced by the tightness of nearby cells, affecting their growth and development.
578 citations,
April 1993 in “Cell” TGFα gene mutation in mice causes abnormal skin, wavy hair, curly whiskers, and sometimes eye inflammation.

The skin is a complex barrier for drug penetration, but understanding its structure and interactions can improve drug delivery methods.
























