 January 2023 in “Applied sciences”
January 2023 in “Applied sciences” Gefitinib and Sasam-Kyeongokgo together significantly reduce cancer growth and improve immune response in mice.
 February 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2009 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that detailed clinical descriptions of seven family cases help understand dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa's symptoms and inheritance.

The case shows the difficulty in diagnosing certain conditions when standard tests are negative.
 April 2015 in “Andrology”
April 2015 in “Andrology” HNG may help prevent the negative effects of chemotherapy on sperm production and white blood cell counts.
 6 citations,
March 1996 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery”
6 citations,
March 1996 in “The American Journal of Cosmetic Surgery” A new hair transplant method creates one appealing scar, uses donor hair better, and speeds up surgery.
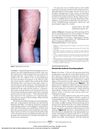 10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Finasteride caused blisters on hands and feet.
 5 citations,
September 2015 in “Nepalese journal of ophthalmology”
5 citations,
September 2015 in “Nepalese journal of ophthalmology” An 11-year-old girl with a rare skin disorder also had cornea issues and dry eye, needing careful management.
 68 citations,
February 1990 in “Journal of Applied Social Psychology”
68 citations,
February 1990 in “Journal of Applied Social Psychology” Bald men are often viewed more negatively and as older than they really are.
 19 citations,
January 2001 in “Dermatology + psychosomatics”
19 citations,
January 2001 in “Dermatology + psychosomatics” The review concluded that male pattern baldness is mostly seen negatively, affecting attractiveness and social appeal.
 15 citations,
January 2016 in “Sustainable development and biodiversity”
15 citations,
January 2016 in “Sustainable development and biodiversity” Using PGPR as biofertilizers can improve soil health and plant growth while reducing reliance on synthetic fertilizers.

Genetic testing can help diagnose skin conditions but needs more research for full effectiveness.
 November 2017 in “Pediatrics in Review”
November 2017 in “Pediatrics in Review” A 4-year-old girl with hair loss was diagnosed with early-onset trichotillomania and improved with behavioral interventions.
 231 citations,
July 2008 in “Nutrition reviews”
231 citations,
July 2008 in “Nutrition reviews” Diet changes can protect against harmful environmental effects on fetal development.
 69 citations,
November 2010 in “Middle East Fertility Society Journal”
69 citations,
November 2010 in “Middle East Fertility Society Journal” PCOS affects women's health by increasing the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and reproductive issues.
 37 citations,
May 2003 in “Journal of Consumer Marketing”
37 citations,
May 2003 in “Journal of Consumer Marketing” The debate on direct-to-consumer pharmaceutical ads continues, with consumers finding them educational and doctors concerned about their impact on patient relationships and medication understanding.
 32 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
32 citations,
February 2008 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” KFSD is a genetic disorder causing hair loss and skin issues, with no effective treatment.
 21 citations,
February 2016 in “Reproductive Biomedicine Online”
21 citations,
February 2016 in “Reproductive Biomedicine Online” The conclusion suggests that PCOS may persist due to genetic traits that, while harmful for female fertility, could have provided survival and reproductive benefits to males.
 12 citations,
November 2014 in “PLOS Computational Biology”
12 citations,
November 2014 in “PLOS Computational Biology” The study concluded that hair growth in mice is regulated by a stable interaction between skin cell types, and disrupting this can cause hair loss.
 9 citations,
February 2016 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
9 citations,
February 2016 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” The conclusion is that self-concept, shame, and emotion regulation are key factors in hoarding disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, and trichotillomania, and should be targeted in treatment and research.
 1 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of S C C J”
1 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of S C C J” Scalp massage reduces stress, increases relaxation, and improves blood circulation.
December 2020 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Trichoscopy helped diagnose a teenage girl's hair loss as monilethrix.
July 2021 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Monilethrix causes different levels of hair loss in family members.
 September 1997 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
September 1997 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Hormonal differences affect male pattern baldness.
 23 citations,
January 2005 in “Nihon Ishinkin Gakkai zasshi”
23 citations,
January 2005 in “Nihon Ishinkin Gakkai zasshi” Nested PCR can reliably identify fungal infections when traditional methods fail.
 1 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
1 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Early hair loss in men and women may indicate a higher risk of heart disease and metabolic problems.
 December 2023 in “JCEM case reports”
December 2023 in “JCEM case reports” A new gene variant causes glucocorticoid resistance in a mother and son.
 179 citations,
September 1998 in “BMJ”
179 citations,
September 1998 in “BMJ” Hair loss in men is common, treatable, but not curable.
 100 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
100 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” Hair loss in men treated best with early medication or transplant, new treatments researched.
 83 citations,
January 2001 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
83 citations,
January 2001 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Clomipramine may significantly reduce hair-pulling in Trichotillomania, but more research is needed on treatments and early onset cases.
 77 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
77 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Environmental factors, hormones, nutrition, and stress all significantly affect skin health and aging.




























