 31 citations,
April 2007 in “Experimental Dermatology”
31 citations,
April 2007 in “Experimental Dermatology” Stress in mice delays hair growth and treatments blocking substance P can partly reverse this effect.
 4 citations,
January 2013 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
4 citations,
January 2013 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Some patients with Alopecia Areata experience itch due to immune cells and enzymes that cause itching.
 115 citations,
November 2004 in “Brain Behavior and Immunity”
115 citations,
November 2004 in “Brain Behavior and Immunity” Stress increases nerve fibers and immune cell activity in mouse skin, possibly worsening skin conditions.
7 citations,
July 2021 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Human skin can be reconnected to nerves using stem cells, which may help with skin health and healing.
 125 citations,
September 2001 in “The FASEB Journal”
125 citations,
September 2001 in “The FASEB Journal” Stress can cause hair loss by negatively affecting hair follicles and this effect might be reversed with specific treatments.
 53 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
53 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” UVB radiation harms hair growth and health, causing cell death and other changes in human hair follicles.
 76 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of Molecular Medicine”
76 citations,
March 2005 in “Journal of Molecular Medicine” Certain mice without specific receptors or mast cells don't lose hair from stress.
 19 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Young Pharmacists”
19 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Young Pharmacists” Alcoholic extract of Eclipta alba may help treat allergies and is safe at high doses.
 159 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology”
159 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology” Stress-related substance P may lead to hair loss and negatively affect hair growth.
 25 citations,
July 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
25 citations,
July 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Imiquimod cream activates hair follicle stem cells and causes early hair growth by changing immune cells and certain protein expressions.
 1 citations,
September 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
September 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks” Hair ages and thins due to factors like inflammation and stress, and treatments like antioxidants and hormones might improve hair health.
3 citations,
July 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Stress may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata by affecting immune responses and cell death in hair follicles.
 108 citations,
July 2004 in “American Journal of Pathology”
108 citations,
July 2004 in “American Journal of Pathology” Stress increases a factor in mice that leads to hair loss, and blocking this factor may prevent it.
 150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology”
150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology” The document concludes that more research is needed to better understand and treat primary cicatricial alopecias, and suggests a possible reclassification based on molecular pathways.
 42 citations,
March 2008 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
42 citations,
March 2008 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” Hormones and neuroendocrine factors control hair growth and color, and more research could lead to new hair treatment options.
 30 citations,
September 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology”
30 citations,
September 2003 in “Experimental Dermatology” Minoxidil helps prevent stress-caused hair loss in mice.
 194 citations,
March 2003 in “American Journal of Pathology”
194 citations,
March 2003 in “American Journal of Pathology” Stress stops hair growth in mice by causing early hair growth phase end and harmful inflammation through a specific nerve-related pathway.
 34 citations,
January 1989 in “Toxicologic Pathology”
34 citations,
January 1989 in “Toxicologic Pathology” A study found that minoxidil can damage the hearts of dogs and pigs, cautioning its use in humans.
 1 citations,
May 2006 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents”
1 citations,
May 2006 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents” No FDA-approved treatments for chemotherapy-induced hair loss existed in 2006; more research was needed.
 September 2004 in “Experimental dermatology”
September 2004 in “Experimental dermatology” Melatonin directly affects mouse hair follicles and may influence hair growth.
 31 citations,
February 2019 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
31 citations,
February 2019 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Caffeine applied to the scalp can protect hair follicles from UV damage.
 3 citations,
May 2017 in “Heliyon”
3 citations,
May 2017 in “Heliyon” Wound healing can help prevent hair loss from chemotherapy in young rats by increasing interleukin-1β signaling.
51 citations,
December 2017 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Stress may trigger hair loss by affecting immune protection in hair follicles.
 2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks” The book details skin conditions in older adults, their link to mental health, cancer treatment importance, hair loss remedies, and managing autoimmune and itchy skin.
 May 2013 in “Springer eBooks”
May 2013 in “Springer eBooks” Skin problems in the elderly are unique and may indicate other diseases, involving changes in skin, hair, nails, and increased cancer risk.
 7 citations,
October 2000 in “Allergo Journal”
7 citations,
October 2000 in “Allergo Journal” Stress may affect hair growth by influencing hair follicle development and could contribute to hair loss.
 March 2024 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
March 2024 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Dandruff is linked to increased T cells and weakened immune protection in hair follicles.
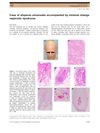 2 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatology” A possible link exists between minimal change nephrotic syndrome and complete hair loss.
 6 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
6 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Certain immune cells are more common on the top of the head and might help predict or treat common hair loss.
124 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” Endocannabinoids help control mast cell activity in human skin.


























