 66 citations,
December 2018 in “Dermatology”
66 citations,
December 2018 in “Dermatology” Both ruxolitinib and tofacitinib are effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata, but relapses are common.
 63 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
63 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical JAK inhibitors may help treat some skin conditions but need more research.
 42 citations,
November 2018 in “Archives of dermatological research”
42 citations,
November 2018 in “Archives of dermatological research” Apremilast was not effective in treating moderate-to-severe alopecia areata.
 18 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
18 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” High and low doses of prednisolone helped 62% of children with severe alopecia regrow hair with some weight gain and mild acne as side effects.
 13 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
13 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that a new system using the SALT score should replace the current alopecia areata classification for better accuracy in assessing severity and prognosis.
 10 citations,
January 2023 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2023 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Baricitinib and deuruxolitinib are effective for treating alopecia areata, but their efficacy depends on the dose.
 9 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
9 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Tofacitinib improves nail conditions in patients with severe hair loss and does not affect hair regrowth.
 January 2023 in “Malaysian Journal of Medical Research”
January 2023 in “Malaysian Journal of Medical Research” Early and proper treatment is crucial for children with allergic conjunctivitis to avoid complications.
 79 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy”
79 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy” Oral tofacitinib can significantly improve recalcitrant lichen planopilaris.
 70 citations,
February 2017 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
70 citations,
February 2017 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Treatment with plasma rich in growth factors improved hair density and thickness for hair loss patients.
 66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib is effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.
 54 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
54 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Tofacitinib is somewhat effective for alopecia areata, but more research is needed on its safety and long-term effects.
 52 citations,
September 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
52 citations,
September 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Ginseng and its compounds may help hair growth and prevent hair loss, but more human trials are needed to confirm this.
 37 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in pharmacology”
37 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in pharmacology” Oral JAK inhibitors are effective and safe for treating alopecia areata but may need ongoing use to keep results.
 32 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
32 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” STAT5 activation is crucial for starting the hair growth phase.
 27 citations,
June 2015 in “Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia”
27 citations,
June 2015 in “Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia” Safflower has been used in traditional medicine for centuries and shows promise in treating heart, brain, and inflammatory conditions, but more research is needed to ensure its safety.
 26 citations,
October 2016 in “Case Reports in Dermatology”
26 citations,
October 2016 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” A man with severe hair loss saw hair and nail improvement after 10 months on tofacitinib without side effects.
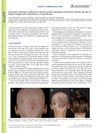 24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib helped a young woman's severe hair loss and arthritis but not her plaque psoriasis.
 23 citations,
October 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
23 citations,
October 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” The current understanding of frontal fibrosing alopecia involves immune, genetic, hormonal factors, and possibly environmental triggers, but more research is needed for effective treatments.
 19 citations,
August 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets”
19 citations,
August 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets” New treatments for hair loss may target specific pathways and generate new hair follicles.
 18 citations,
October 2014 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine”
18 citations,
October 2014 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine” Eating vitamin A affects hair growth and health by changing cell signals in mice.
 16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
16 citations,
July 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Ruxolitinib may help treat hair loss by reducing inflammation, promoting hair growth signals, and protecting hair follicle immunity.
 11 citations,
January 2018 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
11 citations,
January 2018 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib works better and is more tolerable for severe alopecia than conventional treatments and DPCP immunotherapy.
 2 citations,
December 2022 in “PNAS nexus”
2 citations,
December 2022 in “PNAS nexus” SCD-153 shows promise as an effective topical treatment for alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
2 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Stem cells could improve hair growth and new treatments for baldness are being researched.
 2 citations,
April 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
2 citations,
April 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Best treatment for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors and intralesional corticosteroids.
 2 citations,
June 2016 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
2 citations,
June 2016 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Dermatologists often neglect hair disorders due to complexity and lack of clear treatments, impacting patient care and highlighting the need for better education and interest in this area.
 1 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of dermatology and dermatitis”
1 citations,
June 2021 in “Journal of dermatology and dermatitis” Tyrosine kinase inhibitors show promise in treating some skin diseases but their definitive role in dermatology is still unclear.
 February 2024 in “Sohag Medical Journal”
February 2024 in “Sohag Medical Journal” Various local treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but individualized plans and more research are needed.
 August 2023 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology and therapies”
August 2023 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology and therapies” Dupilumab may help hair regrowth in some patients with severe atopic dermatitis, but results vary.






























