 September 2023 in “Journal of Natural Fibers”
September 2023 in “Journal of Natural Fibers” Drying hair with a microfiber towel better maintains hair strength and structure than using a cotton towel or blow-drier.
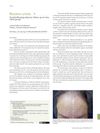 May 2019 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
May 2019 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Frontal fibrosing alopecia mostly affects postmenopausal women, with diagnosis often delayed by 3 years.
 September 1998 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
September 1998 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that individualized treatments for hair issues are effective, certain hair changes can indicate neurocutaneous diseases, specific lotions improve skin health, laser hair removal works but needs more study on long-term effects, men's cosmetics are diverse, peeling is effective but can have side effects, and facial pigmentation is often due to overactive skin cells.
 May 2024 in “Ultramicroscopy”
May 2024 in “Ultramicroscopy” Atomic Force Microscopy is a more accurate way to assess hair damage and the effect of cosmetic treatments.
 February 2024 in “Skin health and disease”
February 2024 in “Skin health and disease” Exosomes could improve skin and hair treatments but are limited by cost, production difficulty, and need for more research.
 4 citations,
July 2022 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
4 citations,
July 2022 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Hair moisture behavior helps tell apart different chemical treatments and reveals insights into hair structure.
 24 citations,
November 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
24 citations,
November 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Hair and scalp disorders significantly affect self-esteem, and using cosmetic products like conditioners and styling aids can improve hair health and appearance.
 April 2021 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery”
April 2021 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery” Hair restoration can be achieved through non-surgical treatments like minoxidil, antiandrogens, phototherapy, and PRP procedures, or through surgical methods like hair transplantation. Continued treatment is needed to maintain results, and full results are visible after 12-18 months.
 2 citations,
July 2020 in “Trends in Urology and Men's Health”
2 citations,
July 2020 in “Trends in Urology and Men's Health” More men are getting cosmetic surgery, with Botox and hair removal being popular, but these procedures have risks.

Lamivudine might reverse hair graying and needs more research for potential treatments.
7 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of dairy science” Bovine milk fats applied to mouse skin can promote hair growth similar to known hair growth treatments.
22 citations,
December 2011 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Over 40% of women have unwanted facial hair, which can affect their self-image, and should be managed with personalized treatment and support.
 21 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
21 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Hair care products don't cause hair loss if used correctly.
March 2005 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Adding amino acids to damaged hair can improve its strength and appearance.
 3 citations,
June 2007 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 2007 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Using the right hair care products can improve hair health and help manage hair disorders.
 August 2024 in “Cosmetics”
August 2024 in “Cosmetics” Caffeine is beneficial for skin and hair treatments but needs better delivery methods to penetrate deeper skin layers.
 1 citations,
January 1967 in “The BMJ”
1 citations,
January 1967 in “The BMJ” The document concludes that while some hair and scalp disorders can be treated, hair loss from destroyed follicles is permanent, and damaged hair can only regrow naturally.
 September 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
September 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Biologicals are increasingly used in medicine and cosmetics, especially for skin and hair treatments, but more research is needed.
 48 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics”
48 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics” Some treatments can help with hair regrowth in alopecia areata, but results vary and long-term use is often needed without changing the disease's outcome.

The study concluded that the developed method can show how argan, avocado, and coconut oils penetrate and change hair, suggesting these oils are effective in hair treatments.
 February 2008 in “Basic and clinical dermatology”
February 2008 in “Basic and clinical dermatology” Photographic imaging is crucial for documenting and managing hair loss, requiring careful preparation and standardization to be effective.
January 2023 in “Applied sciences” Equisetum debile extracts may help with skin whitening, anti-wrinkle, and anti-hair loss treatments.
 May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine”
May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine” Excessive hair growth in women, often from high androgen levels, is usually caused by PCOS, and can be treated with hair removal, medication, and possibly weight loss.
 4 citations,
August 2011 in “Aktuelle Dermatologie”
4 citations,
August 2011 in “Aktuelle Dermatologie” Topical melatonin is a safe treatment that may reduce hair loss in people with androgenetic alopecia.

Using microneedling with PRP improves skin and hair conditions more than microneedling alone.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Telogen Effluvium is a common, usually reversible hair loss condition, often improved by removing the trigger and possibly treated with various products, though their effectiveness is uncertain.
 10 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of General Internal Medicine”
10 citations,
May 1995 in “Journal of General Internal Medicine” Most women with excessive hair growth have PCOS; treatment varies and focuses on preventing new hair, with electrolysis as the only permanent removal method.
 82 citations,
May 2016 in “Best Practice & Research in Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology”
82 citations,
May 2016 in “Best Practice & Research in Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology” The conclusion is that managing androgen excess requires long-term treatment, including hormonal contraceptives and androgen blockers, with follow-up after six months.
July 2002 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Laser and Eflornithine are more effective for hair removal than traditional methods.
 40 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
40 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Brazilian keratin treatments can straighten hair but may contain harmful formaldehyde.

























