 9 citations,
July 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
July 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Brodalumab effectively treated a man's severe hand and foot psoriasis.
 35 citations,
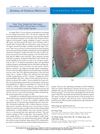
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology”
35 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology” A cancer patient died from a severe skin reaction after taking the drug cetuximab.
 10 citations,
January 2003 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
10 citations,
January 2003 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Hydroxychloroquine helped improve scleromyxoedema in patients, but caused side effects in some.
[object Object]  20 citations,
April 1999 in “British journal of plastic surgery”
20 citations,
April 1999 in “British journal of plastic surgery” Ruby laser hair removal significantly reduces hair density.
 17 citations,
January 2019 in “International journal of biological sciences”
17 citations,
January 2019 in “International journal of biological sciences” Researchers used CRISPR/Cas9 to create a goat with a gene that increased cashmere production by 74.5% without affecting quality.
 2 citations,
February 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
February 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Bimatoprost solution 0.03% is effective for treating sparse eyelashes.
 August 2023 in “Physician's journal of medicine”
August 2023 in “Physician's journal of medicine” Hashimoto thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease that can lead to an underactive thyroid and is treated with medication and sometimes diet changes or surgery.
 2 citations,
January 2022 in “Experimental Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Experimental Dermatology” GDNF signaling helps in hair growth and skin healing after a wound.
 91 citations,
December 2010 in “Stem Cells”
91 citations,
December 2010 in “Stem Cells” Wnt signaling helps control how brain stem cells divide and is important for brain repair after injury.
10 citations,
April 2014 in “Molecular and Clinical Oncology” Alopecia areata can be an early sign of Hodgkin’s lymphoma and may improve with lymphoma treatment.
 6 citations,
January 2010 in “Springer eBooks”
6 citations,
January 2010 in “Springer eBooks” SA linked to mitochondrial issues and oxidative stress, while AGA involves disrupted hair growth genes.
 139 citations,
February 2010 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
139 citations,
February 2010 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Transplant success has improved with better immunosuppressive drugs and donor matching.
 6 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Cellular Physiology”
6 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Cellular Physiology” Human scalp fat stem cells showed improved cartilage-like development on a special scaffold with freeze-thaw treatment.
 14 citations,
May 2013 in “American Journal of Physiology-endocrinology and Metabolism”
14 citations,
May 2013 in “American Journal of Physiology-endocrinology and Metabolism” Removing myelin protein zero-like 3 in mice leads to better metabolism and resistance to obesity.
 5 citations,
July 2021 in “Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology”
5 citations,
July 2021 in “Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology” Melatonin may protect ear cells from damage caused by nicotine.
107 citations,
April 2014 in “The Plant cell” The CAP1 gene helps control ammonium levels and is necessary for the proper growth of root hairs in Arabidopsis.
[object Object]  July 1997 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 1997 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Finasteride significantly increases scalp hair and prevents hair loss in young and middle-aged men.
 33 citations,
December 2015 in “Neuroendocrinology”
33 citations,
December 2015 in “Neuroendocrinology” Finasteride treatment changes brain steroid levels and receptors, affecting brain function even after stopping treatment.
 1 citations,
June 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
June 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Activating β-catenin in mammary cells leads to changes that cause early-stage abnormal growths similar to skin structures.
26 citations,
July 2011 in “PubMed” Treating H. pylori infection might help cure alopecia areata.
 8 citations,
August 2007 in “Histopathology”
8 citations,
August 2007 in “Histopathology” Different growth patterns in thyroid tumors are influenced by where cell growth and death occur.
 2 citations,
November 2011 in “InTech eBooks”
2 citations,
November 2011 in “InTech eBooks” Most adrenal cortex tumors are benign and non-secreting, but proper diagnosis and treatment are important due to the rare possibility of cancer.
23 citations,
December 2013 in “Molecular cancer therapeutics” Breast cancer treatments work better with AR activation, improving results and reducing side effects.
 29 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncology and therapy”
29 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncology and therapy” The document provides advice on how to recognize and treat skin-related side effects of cancer drugs known as EGFR inhibitors.
 March 2010 in “Anti-inflammatory & anti-allergy agents in medicinal chemistry”
March 2010 in “Anti-inflammatory & anti-allergy agents in medicinal chemistry” Biologic agents can be effective for rheumatic diseases but have risks like infections and require careful monitoring and patient information.
 18 citations,
April 2011 in “International Journal of Molecular Medicine”
18 citations,
April 2011 in “International Journal of Molecular Medicine” Dihydrotestosterone causes p27 protein breakdown in ovarian and breast cancer cells by binding with SKP2.
 38 citations,
December 2009 in “Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology”
38 citations,
December 2009 in “Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology” The conclusion suggests that prostate cancer should be classified by castration status and that new therapies targeting androgen receptor signaling show promise.
 48 citations,
June 2014 in “Neurobiology of Disease”
48 citations,
June 2014 in “Neurobiology of Disease” The study suggests that motor neurons created from stem cells of patients with spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy show signs of the disease, including changes in protein levels and cell functions.
 8 citations,
April 2015 in “Transboundary and Emerging Diseases”
8 citations,
April 2015 in “Transboundary and Emerging Diseases” A hospital outbreak of catheter infections in calves was caused by a bacteria from a beef herd, leading to longer hospital stays, more drug use, and calf deaths.
 March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements”
March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements” Gene variation affects prostate issues and hair loss.


























