January 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking certain pathways with kinase inhibitors may help treat cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
1 citations,
September 2022 in “Journal of the Egyptian Womenʼs Dermatologic Society” A rare scalp infection in a 66-year-old woman was successfully treated, leading to full hair regrowth.
 September 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
September 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The patient responded well to treatment with no disease progression.
[object Object]  August 2023 in “International Medical Case Reports Journal”
August 2023 in “International Medical Case Reports Journal” Acne necrotica can be effectively treated with topical cream and antibiotics.

PRP therapy effectively treats hair loss, wrinkles, scars, ulcers, and skin pigmentation disorders.
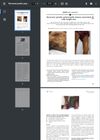 October 2022 in “JAAD case reports”
October 2022 in “JAAD case reports” A man with itchy skin lesions and weight loss was diagnosed with a rare skin condition linked to a pancreatic tumor.
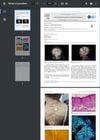 September 2022 in “International journal of infectious diseases”
September 2022 in “International journal of infectious diseases” A woman with a rare scalp infection was cured after one month of medication.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
May 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking DPP4 can potentially speed up hair growth and regeneration, especially after injury or in cases of hair loss.
9 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Pili torti is a rare condition where hair is twisted and breaks easily, often linked to genetic disorders or other health issues.
[object Object] 2 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Gasdermin A3 causes hair follicle stem cells to activate too early, leading to hair loss.
40 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” CLASI is a valid tool for assessing skin activity and damage in lupus patients.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with limited and variable treatment effectiveness.
 89 citations,
February 2002 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
89 citations,
February 2002 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” A premenopausal woman had hair loss and skin issues, treated with topical steroids.
 61 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
61 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” The cause of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is unclear, diagnosis involves clinical evaluation and various treatments exist, but their effectiveness is uncertain.
 44 citations,
July 2005 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery”
44 citations,
July 2005 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery” Hair transplantation successfully treated a woman's hair loss caused by a tight ponytail.
 28 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
28 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Chinese patients with primary cicatricial alopecia often have folliculitis decalvans, benefit from treatment, but may experience relapse, with dermoscopy being a useful diagnostic tool.
 12 citations,
January 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
12 citations,
January 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” A mother and daughter with similar hair loss conditions and identical HLA types suggest a genetic link between the conditions.
 9 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of Dermatology” Asian patients with Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia often lose eyebrow hair and respond well to combined antiandrogen or antimalarial and topical treatments.
 1 citations,
August 2019 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2019 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Immunotherapy can help treat severe alopecia areata.
 329 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
329 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a hair loss condition in postmenopausal women, similar to lichen planopilaris, with ineffective treatments.
 150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology”
150 citations,
October 2010 in “The American Journal of Pathology” The document concludes that more research is needed to better understand and treat primary cicatricial alopecias, and suggests a possible reclassification based on molecular pathways.
 123 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
123 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The study found that Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia affects a broader age range of women and early treatment can help stop hair loss.
 80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine”
80 citations,
April 2018 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine” Lichen Planopilaris and Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia may help us understand hair follicle stem cell disorders and suggest new treatments.
 68 citations,
May 2016 in “Experimental dermatology”
68 citations,
May 2016 in “Experimental dermatology” FFA's causes may include environmental triggers and genetic factors.
 65 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
65 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that early recognition and treatment of primary cicatricial alopecia is crucial to prevent permanent hair loss.
 62 citations,
January 2003 in “Dermatology”
62 citations,
January 2003 in “Dermatology” Sunlight worsens hair loss; protect scalp.
 51 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
51 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” The document concludes that surgery is a preferred treatment for cicatricial alopecia, with the method chosen based on individual factors and may require multiple sessions and careful postoperative care.
 50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Alopecia Areata has no guaranteed treatment for hair regrowth, but options like corticosteroids and minoxidil are used, with future research focusing on genetic and immune therapies.
 43 citations,
November 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
43 citations,
November 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” FAGA diagnosis uses blood tests and trichoscopy, with treatments like topical minoxidil, oral anti-androgens, and hormone-modulating drugs.
 40 citations,
September 2017 in “F1000Research”
40 citations,
September 2017 in “F1000Research” Oral minoxidil effectively reduces hair shedding in women with CTE, with no major side effects.
























