 September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A 14-year-old boy was diagnosed with a rare hair condition that may lead to hair thinning and has no known effective treatments.
 3 citations,
February 2022 in “Frontiers in Genetics”
3 citations,
February 2022 in “Frontiers in Genetics” The LncRNA AC010789.1 slows down hair loss by promoting hair follicle growth and interacting with miR-21 and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
 29 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
29 citations,
February 2017 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” Women with excessive male-pattern hair growth should get a full hormone check-up to find and treat any underlying issues, considering both medical and emotional aspects.
 1 citations,
October 2012 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2012 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A Korean girl developed kinky hair without known cause or effective treatment.
 January 2008 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2008 in “Springer eBooks” Thyroid disease can cause hair loss and treating thyroid problems might help with hair disorders.
 67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Hirsutism is excessive hair growth in women often caused by polycystic ovarian syndrome, and identifying the cause is important for managing associated health risks.
 23 citations,
July 1993 in “Pharmacotherapy”
23 citations,
July 1993 in “Pharmacotherapy” Finasteride treats enlarged prostate and baldness, but may cause limited urinary improvement and sex-related side effects.
 67 citations,
November 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
67 citations,
November 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that careful evaluation is key to diagnose and treat women with hair loss, with tests for thyroid, iron, and hormones as needed.
 19 citations,
March 1996 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
19 citations,
March 1996 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Balding hair follicle cells are smaller, grow less well, and need more effort to culture than non-balding cells.
 11 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
11 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” The conclusion is that treatments like finasteride and minoxidil can prevent baldness progression and improve hair density, but more research is needed on other therapies.
January 2021 in “Menoufia Medical Journal” People with early-onset androgenetic alopecia may have a higher risk of heart disease due to abnormal blood lipid levels.
 20 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
20 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Most cases of excessive hair growth in women are caused by polycystic ovarian syndrome and are linked to higher free testosterone levels.
 8 citations,
June 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
8 citations,
June 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Men with early hair loss have lower vitamin D levels.
 10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine”
10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine” The article explains how to identify and treat excessive hair growth in women, which can be distressing and may signal other health problems.
November 2022 in “Cureus” New biomaterial treatments for baldness show promise, with options depending on patient needs.
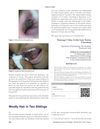 January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Two siblings have a rare genetic condition causing curly, coarse hair.

The conclusion is that endocrinology significantly impacts medicine with various common medications used for treatment.
 April 2024 in “Prostate international”
April 2024 in “Prostate international” Male pattern baldness does not cause an increased risk of prostate cancer.
 54 citations,
May 1998 in “Urology”
54 citations,
May 1998 in “Urology” Men with enlarged prostates often have more severe baldness.
 98 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
98 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Prolactin affects hair growth and skin conditions, and could be a target for new skin disease treatments.
 12 citations,
November 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document explains that hirsutism, often caused by hormonal issues, can be managed with treatment to improve both physical appearance and mental health.

Detailed history and physical examination are crucial for diagnosing hair loss.
 January 2024 in “Biology of sex differences”
January 2024 in “Biology of sex differences” Dihydrotestosterone makes arteries stiffer in female mice by reducing estrogen receptor expression.
 December 2000 in “Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine”
December 2000 in “Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine” Antiandrogen therapy may help treat hidradenitis suppurativa.
 3 citations,
December 2000 in “Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine”
3 citations,
December 2000 in “Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine” Antiandrogen therapy may be beneficial for women with hidradenitis suppurativa.
 5 citations,
July 2000 in “Southern Medical Journal”
5 citations,
July 2000 in “Southern Medical Journal” Male pattern baldness is often genetic and linked to a hormone, with treatments like finasteride and minoxidil being effective for some men.
 11 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
11 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Caffeine may help hair growth in hereditary hair loss.
 3 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry”
3 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry” Finasteride may affect PNMT, causing side effects.
 September 2024 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
September 2024 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” Combining PRP with minoxidil and finasteride is the most effective treatment for male hair loss.



























