 June 2024 in “Trends in Urology & Men s Health”
June 2024 in “Trends in Urology & Men s Health” Post-finasteride syndrome is rare but serious and should be taken seriously.

Finasteride may cause memory problems by damaging the hippocampus.
 August 2009 in “Reactions Weekly”
August 2009 in “Reactions Weekly” Finasteride caused breast enlargement in two men, which improved after stopping the medication.
[object Object]  March 2009 in “The Journal of Urology”
March 2009 in “The Journal of Urology” Low dose finasteride causes only small changes in PSA levels in older men with BPH.
May 2018 in “Hair transplant forum international” Topical finasteride promotes hair growth with minimal side effects but needs more research for women and optimal use.
 April 2006 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
April 2006 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Oral finasteride, combined with drospirenone, improved hair loss in 62% of premenopausal women, with no reported side effects.
 198 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
198 citations,
October 2011 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Use minoxidil for hair loss; finasteride and dutasteride for men, dutasteride for women.
 72 citations,
January 2001 in “Drugs”
72 citations,
January 2001 in “Drugs” Minoxidil and finasteride treat hair loss; more research needed for other options.
 54 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
54 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Low level laser therapy works best for hair loss, followed by PRP, finasteride, and minoxidil.
 2 citations,
March 2015 in “World journal of acupuncture-moxibustion”
2 citations,
March 2015 in “World journal of acupuncture-moxibustion” Traditional Chinese medicine techniques like catgut embedment, moxibustion, and bloodletting showed better results for treating hair loss than the drug finasteride.
 January 2013 in “Hair transplant forum international”
January 2013 in “Hair transplant forum international” Minoxidil and finasteride are effective for male hair loss; minoxidil also helps female hair loss, with some treatments needing more research.
July 2004 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” January 2004 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)”  88 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
88 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Minoxidil and finasteride effectively treat hair loss.
 29 citations,
September 2014 in “Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Obesity”
29 citations,
September 2014 in “Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Obesity” Finasteride and dutasteride effectively treat hair loss in men and women, but may cause side effects like low libido and depression.
 4 citations,
May 2002 in “Therapeutische Umschau”
4 citations,
May 2002 in “Therapeutische Umschau” AGA treated with finasteride, minoxidil, and hair transplantation.
1 citations,
July 2020 in “Reviews in separation sciences”  1 citations,
January 2011
1 citations,
January 2011 The document concludes that androgenetic alopecia is common, has a genetic link, and can be diagnosed and treated with medications like finasteride and minoxidil.
 1 citations,
July 1997 in “Inpharma Weekly”
1 citations,
July 1997 in “Inpharma Weekly” Finasteride improves hair growth and satisfaction in men with male pattern baldness but may cause sexual side effects.
 November 2020 in “Elsevier eBooks”
November 2020 in “Elsevier eBooks” Antiandrogens and androgen inhibitors like spironolactone, finasteride, and dutasteride can treat hair loss and skin conditions, but they have risks and side effects, including potential harm to pregnant women and risks of cancer and heart issues. Herbal remedies also have antiandrogenic effects but lack safety validation.

The article concludes that understanding the causes of hair loss and using continuous treatments like minoxidil and finasteride can help manage it, despite potential side effects.
 February 2013 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2013 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Using hair loss drugs finasteride and dutasteride may cause sexual side effects.
January 2022 in “Springer eBooks” [object Object] July 2005 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”  22 citations,
August 2015 in “Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews”
22 citations,
August 2015 in “Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews” The study aims to find the best treatment for central serous chorioretinopathy by comparing various options.
 1 citations,
September 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
1 citations,
September 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” More research is needed to find the best treatment for dissecting cellulitis of the scalp.
 June 1996 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -)”
June 1996 in “Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -)” The document summarizes medical findings on topics like heart rhythm treatment, sleep apnea therapy, and various health conditions and treatments.
February 2014 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”  1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Hair loss, known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is often caused by hormones and can be diagnosed using noninvasive techniques. Treatments include topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, with new treatments being explored. There may also be a link between this type of hair loss and heart disease risk.
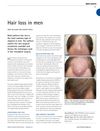 May 2013 in “Trends in Urology & Men's Health”
May 2013 in “Trends in Urology & Men's Health” Male-pattern hair loss is normal, often involves hormone effects on hair follicles, and can be treated with medication or surgery, but new treatments are being researched.























