 March 2005 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
March 2005 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” A new method helps understand hair shine and various products improve hair care.

Hair loss causes emotional distress, leading to high spending on treatments, with Minoxidil and Propecia being common but having side effects.
37 citations,
October 2015 in “PeerJ” Perming significantly changes hair's molecular structure, while shampoo and conditioner do not.
5 citations,
February 2022 in “Animals” Sodium sulfide slows wound healing, while electric shaving is the safest for preoperative hair removal.
 72 citations,
October 1998 in “Baillière's clinical endocrinology and metabolism”
72 citations,
October 1998 in “Baillière's clinical endocrinology and metabolism” Long-term testosterone therapy can cause hormone suppression, affect prostate and heart health, and alter physical characteristics, but does not increase prostate cancer risk and needs more research for full risk assessment.
 14 citations,
January 2006 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
14 citations,
January 2006 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Alopecia areata can look like frontal fibrosing alopecia, making diagnosis hard.
 13 citations,
December 2006 in “Journal of experimental animal science”
13 citations,
December 2006 in “Journal of experimental animal science” Interferon gamma alone can't cause alopecia areata in C3H/HeJ mice.
 3 citations,
January 2010 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
3 citations,
January 2010 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” No treatment fully stops excessive hair growth in women, but various methods can help manage it effectively.
 2 citations,
March 2013 in “Phytotherapy Research”
2 citations,
March 2013 in “Phytotherapy Research” Ascorbigen increases hair cell growth in a lab setting but does not prevent hair loss from chemotherapy in mice.
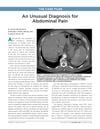 October 2018 in “Emergency medicine news”
October 2018 in “Emergency medicine news” A 65-year-old man with sudden abdominal pain and seizures was diagnosed with a rare, non-traumatic splenic rupture and treated without surgery.
 March 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
March 2014 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The document discusses how to identify and manage common skin conditions in children.
 57 citations,
April 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
57 citations,
April 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Vitamin D receptor is crucial for starting hair growth after birth.
 33 citations,
May 2006 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
33 citations,
May 2006 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” PTHrP and its receptor can control blood vessel growth and hair development in mouse skin.
 19 citations,
September 2004 in “Reviews in gynaecological practice”
19 citations,
September 2004 in “Reviews in gynaecological practice” Effective hirsutism management requires identifying the cause, combining new and traditional treatments, and setting realistic expectations for patients.
 17 citations,
June 2011 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
17 citations,
June 2011 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Hair transplantation is an effective way to restore eyebrows.
 12 citations,
June 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders”
12 citations,
June 2016 in “Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders” Some skin diseases and their treatments can negatively affect male fertility.
 11 citations,
February 2008 in “British journal of nursing”
11 citations,
February 2008 in “British journal of nursing” Idiopathic hirsutism causes excessive hair growth in women, can be treated with medication and hair removal, but cannot be fully reversed.
 10 citations,
January 2005 in “Dermatology”
10 citations,
January 2005 in “Dermatology” Baldness may be linked to heart disease, but the evidence isn't strong enough to consider it a major risk factor.
 9 citations,
May 2021 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
9 citations,
May 2021 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Home-based skin care devices are generally safe and effective for hair removal, promoting hair growth, treating wrinkles and acne, but results for psoriasis treatment are mixed.
 9 citations,
September 2000 in “Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America”
9 citations,
September 2000 in “Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America” Hirsutism causes significant psychological distress in women.
 8 citations,
January 2009 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
8 citations,
January 2009 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Finasteride can cause rare breast growth side effect, with varying recovery after stopping.
 January 2024 in “Deleted Journal”
January 2024 in “Deleted Journal” Essential oils may help hair health but lack strong scientific proof and can cause allergic reactions.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Obesity can weaken the skin's ability to fight infections because fat cells stop and reduce the infection-fighting properties of nearby stem cells.
 June 2012 in “Springer eBooks”
June 2012 in “Springer eBooks” Skin changes can indicate starvation and nutritional deficiencies in anorexia nervosa.
 August 2021 in “Acta Haematologica Polonica”
August 2021 in “Acta Haematologica Polonica” Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides has a worse prognosis than other types, with survival rates varying significantly based on subtype and organ involvement.
 May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine”
May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine” Excessive hair growth in women, often from high androgen levels, is usually caused by PCOS, and can be treated with hair removal, medication, and possibly weight loss.
 173 citations,
January 2014 in “Nature Cell Biology”
173 citations,
January 2014 in “Nature Cell Biology” Wnt signaling controls whether hair follicle stem cells stay inactive or regenerate hair.
 147 citations,
April 1994 in “Drug Safety”
147 citations,
April 1994 in “Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause hair loss or increase hair growth, but these effects are usually reversible when the drug is stopped.
 137 citations,
June 2005 in “Climacteric”
137 citations,
June 2005 in “Climacteric” Estrogen loss during menopause worsens skin health, but hormone replacement therapy may improve it, though more research is needed.
 130 citations,
September 1990 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
130 citations,
September 1990 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Flutamide effectively reduced excessive hair growth and improved related symptoms in hirsutism patients without significant side effects.




























