TLDR Hair loss causes emotional distress, leading to high spending on treatments, with Minoxidil and Propecia being common but having side effects.
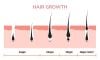
Hair loss, while not life-threatening, caused significant emotional distress, leading sufferers to spend billions on treatments like drugs, vitamins, and special shampoos. Conventional treatments included drug therapy and hair transplants, with Minoxidil and Propecia (Finasteride) being the only FDA-approved drugs for men, and Minoxidil for women. These drugs were effective for balding on the vertex region of the scalp but had concerns about long-term effects and side effects, prompting interest in alternative remedies like herbal medicine.
 33 citations
,
January 2016 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
33 citations
,
January 2016 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Taking 1 mg of finasteride daily can increase hair count and improve hair appearance, but it may have side effects on sexual function and a potential risk of prostate cancer. It may not be effective for postmenopausal women unless taken in higher doses.
 19 citations
,
January 1997 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
19 citations
,
January 1997 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Most treatments for hair loss in 1997 were not effective for most people, and maintaining hair growth was difficult.
 13 citations
,
July 2001 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
13 citations
,
July 2001 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Inflammation and Demodex mites might contribute to hair loss, and targeting them could help treat it.
 9 citations
,
February 2005 in “The Journal of Men's Health & Gender”
9 citations
,
February 2005 in “The Journal of Men's Health & Gender” Finasteride effectively treats male hair loss, increasing length and thickness.

The new treatment regimen was effective in promoting significant hair growth in all 15 male patients with androgenic alopecia.