 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of clinical & experimental dermatology research” Both fat-derived stem cells and platelet-rich plasma are effective and safe for hair loss, but stem cells give better results with more side effects.
 1 citations,
July 2019 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2019 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil was more effective than laser therapy for hair loss, and the report also highlighted the need for more research on PRP for a different hair loss condition, the impact of social media on alopecia views, and a warning on turmeric causing nail discoloration.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Some drugs can cause reversible hair loss, but certain chemotherapy drugs may lead to permanent hair loss; drugs can also change hair color and texture.
1 citations,
January 2023 in “Chemical Engineering Journal”  January 2024 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
January 2024 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” AP-2α and AP-2β are crucial for healthy skin and hair.
 2 citations,
August 2023 in “Life”
2 citations,
August 2023 in “Life” Bioinspired polymers are promising for advanced medical treatments and tissue repair.
 August 2024 in “Cosmetics”
August 2024 in “Cosmetics” K18® and Olaplex® both effectively repair bleached hair, improving its strength, smoothness, and overall health.
 January 2024 in “Biochemical genetics”
January 2024 in “Biochemical genetics” The research found specific genes and proteins that affect how fast chickens' feathers grow, which is not solely determined by traditional inheritance patterns.
December 2023 in “Animals” The research found genes and miRNAs that may control hair growth in Forest Musk Deer.
 5 citations,
May 2022 in “Biomedicines”
5 citations,
May 2022 in “Biomedicines” Botryococcus terribilis and its compounds may promote hair growth and improve hair health.
September 2023 in “World Rabbit Science” The FRZB gene slows hair growth in rabbits.
Different genes and pathways are active in yak skin and hair cells, affecting hair growth and immune responses.
56 citations,
September 2010 in “Veterinary pathology” Certain mouse strains develop a skin condition similar to a human hair loss disease due to genetic defects.
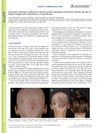 24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib helped a young woman's severe hair loss and arthritis but not her plaque psoriasis.
 3 citations,
August 2022 in “Curēus”
3 citations,
August 2022 in “Curēus” The SARS-CoV-2 vaccine may be linked to triggering autoimmune conditions like Alopecia Areata.
 August 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Baricitinib effectively promotes hair regrowth in both scalp and nonscalp areas for alopecia areata universalis patients.
 222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight”
222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight” Tofacitinib is safe and effective for severe alopecia areata, but hair loss may return 2 months after stopping treatment.
 68 citations,
November 2015 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology”
68 citations,
November 2015 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” Blocking IL-12/IL-23p40 helped reverse severe hair loss in patients.
 15 citations,
May 2017 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
15 citations,
May 2017 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” High-dose corticosteroids and methotrexate had a modest effect on severe childhood alopecia, but side effects and relapse were concerns.
 2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” Early onset, severe types, nail changes, family history, and body hair loss worsen alopecia areata prognosis; sticking to treatment helps.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with certain allergic conditions or higher white blood cell counts have more severe hair loss, and treating hair and nail side effects early in melanoma therapy can improve quality of life.
 January 2007 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2007 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Intramuscular triamcinolone and pulse therapy with oral predonine are effective for alopecia areata with manageable side effects, but better relapse prevention is needed.
 163 citations,
November 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
163 citations,
November 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Low iron levels may be linked to some types of hair loss in women.
 19 citations,
January 2018
19 citations,
January 2018 Most people with alopecia areata have nail changes, which are common but don't greatly affect their quality of life.
 12 citations,
June 2010 in “Journal of dermatology”
12 citations,
June 2010 in “Journal of dermatology” Some patients with severe alopecia areata developed skin darkening from their treatment, which may indicate a less effective response to the therapy.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The study found that severe alopecia areata affects any age, treatments often give temporary results, and some factors predict worse outcomes.
 35 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
35 citations,
November 2010 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Dilated follicular infundibula and increased catagen/telogen follicles are key indicators for diagnosing alopecia areata.
 7 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
7 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Less than a quarter of alopecia areata cases were unusual forms or had paradoxical regrowth.
 63 citations,
May 2017 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
63 citations,
May 2017 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” People with alopecia areata often have lower levels of vitamin D, zinc, and folate, but more research is needed to understand if supplements can help treat it.
 18 citations,
April 2013 in “Inflammatory Bowel Diseases”
18 citations,
April 2013 in “Inflammatory Bowel Diseases” People with Inflammatory Bowel Disease often lose hair due to stress, medication side effects, or lack of nutrients, and treatment depends on the specific cause.
























