71 citations,
February 2012 in “The American Journal of Human Genetics” A specific ATR gene mutation is linked to a hereditary oropharyngeal cancer syndrome.
 126 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
126 citations,
January 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document concludes that understanding hair structure is key to diagnosing hair abnormalities and recommends gentle hair care for management.
12 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian dermatology online journal” The document reports a unique case of woolly hair with a combination of conditions not previously seen together.
 November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” Understanding normal hair growth and loss in children is key to diagnosing and treating hair disorders.
 January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal”
January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal” A child with ectodermal dysplasia-syndactyly syndrome has a new mutation in the NECTIN4 gene.
163 citations,
October 2001 in “EMBO journal” Overexpressing follistatin in mice delays wound healing and reduces scar size.
 5 citations,
October 1984 in “The BMJ”
5 citations,
October 1984 in “The BMJ” Up to 50% of scalp hair can be lost before it appears thin, and treatment is only needed for hair loss caused by diseases or deficiencies.
3 citations,
January 2020 in “International journal of trichology” Congenital triangular alopecia is a hair loss condition present from birth or early childhood with no effective treatment needed.
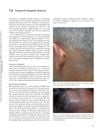 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Temporal triangular alopecia is a lifelong condition with hairless patches on the side of the head that may be present from birth.
 24 citations,
July 1983 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
24 citations,
July 1983 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Tigason improved hair growth in a boy with monilethrix without side effects.
 18 citations,
June 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
18 citations,
June 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Women experience various skin issues at different life stages, requiring careful treatment and awareness.
 23 citations,
November 2001 in “Archives of Dermatology”
23 citations,
November 2001 in “Archives of Dermatology” Genetic discoveries are key for understanding, diagnosing, and treating inherited hair and nail disorders.
 18 citations,
December 2006 in “Clinical dysmorphology”
18 citations,
December 2006 in “Clinical dysmorphology” A 2-year-old boy with a rare brain malformation may have Gomez–López-Hernández syndrome.
 7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2008 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that various childhood hair and nail disorders exist, some may improve on their own, and advances in genetics and immunology could enhance treatment and counseling.
9 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Pili torti is a rare condition where hair is twisted and breaks easily, often linked to genetic disorders or other health issues.
 56 citations,
March 2010 in “Journal of Dermatology”
56 citations,
March 2010 in “Journal of Dermatology” Most cases of Temporal Triangular Alopecia are found in early childhood and may be related to genetic conditions.
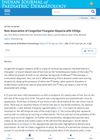 April 2024 in “Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology”
April 2024 in “Indian Journal of Paediatric Dermatology” Congenital triangular alopecia and vitiligo can occur together, but treatment for one may not affect the other.
 7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Most hair loss in children is caused by a few common conditions and is easy to diagnose, but rare types require careful evaluation.
 December 2020 in “TURKDERM”
December 2020 in “TURKDERM” A 3-year-old boy was diagnosed with a rare, non-scarring hair loss condition called temporal triangular alopecia.
 16 citations,
June 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
16 citations,
June 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery” A 17-year-old boy with Temporal Triangular Alopecia successfully grew new hair after a hair restoration surgery using follicular unit transplantation.

Researchers found a genetic link for hereditary hair loss but need more analysis to identify the exact gene.
 July 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2005 in “British Journal of Dermatology” New gene mutations linked to skin conditions were found, bacteria and chemicals may worsen acne, a dog mutation could exist in humans, virus-like elements might be involved in psoriasis, and a vitamin D3 treatment doesn't prevent chemotherapy-related hair loss.
 1 citations,
November 2017 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs”
1 citations,
November 2017 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs” Scientists now better understand the genetics of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, leading to more accurate diagnoses and potential new treatments.
 10 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
10 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A mutation in the FAM83G gene is linked to skin and hair abnormalities in two related individuals.
 32 citations,
February 2008 in “Developmental dynamics”
32 citations,
February 2008 in “Developmental dynamics” Mice without the Sp6 gene have problems developing several body parts, including hair, teeth, limbs, and lungs.
 11 citations,
May 2011 in “World Journal of Pediatrics”
11 citations,
May 2011 in “World Journal of Pediatrics” The document emphasizes the importance of correctly identifying and classifying genetic hair disorders to help diagnose related health conditions.

 20 citations,
July 2013 in “European Journal of Oral Sciences”
20 citations,
July 2013 in “European Journal of Oral Sciences” A new PAX9 gene mutation causes missing teeth and hair problems, but not skin or nail issues.
 January 2022 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
January 2022 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” Uncombable hair syndrome causes frizzy hair and can affect the nervous system, eyes, and ears, often co-occurring with other hair, skin, nail, and teeth conditions, and is linked to three specific gene mutations.
 4 citations,
December 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
4 citations,
December 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A new mutation in the K6b gene caused a girl's late-appearing nail condition.
























