A Novel Pathogenic Variant of NECTIN4 Gene in a Child With Ectodermal Dysplasia-Syndactyly Syndrome
January 2023
in “
Indian dermatology online journal
”
Ectodermal Dysplasia-Syndactyly Syndrome 1 EDSS1 NECTIN4 gene nectin-4 hair morphogenesis hair cycling ectodermal organogenesis sparse hair brittle hair dry scalp hair nail dystrophy cutaneous syndactyly hair growth hair cycle skin development thin hair weak hair dry hair nail problems webbed fingers
TLDR A child with ectodermal dysplasia-syndactyly syndrome has a new mutation in the NECTIN4 gene.
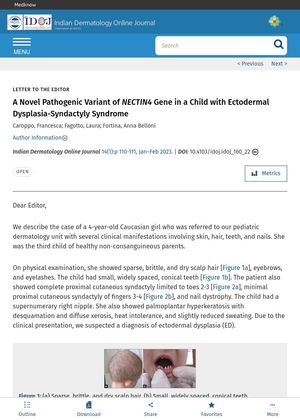
The document describes the case of a 4-year-old girl diagnosed with Ectodermal Dysplasia-Syndactyly Syndrome 1 (EDSS1), a rare inherited disorder characterized by alterations in hair, nails, sweat glands, or teeth, and syndactyly of fingers and/or toes. The diagnosis was confirmed through genetic analysis, which revealed a novel homozygous missense variant of the NECTIN4 gene, c.1117C>T p.Arg373Ter, not previously described in EDSS1 patients. The NECTIN4 gene encodes the cell adhesion protein nectin-4, which plays a crucial role in hair morphogenesis and cycling, and its mutation leads to defective ectodermal organogenesis. The patient's symptoms included sparse, brittle, and dry scalp hair, small, widely spaced, conical teeth, cutaneous syndactyly, and nail dystrophy. The study emphasizes the importance of molecular genetic testing in patients with suspected ED to achieve the correct diagnosis and identify the specific syndrome.
