 December 2024 in “Frontiers in Genetics”
December 2024 in “Frontiers in Genetics” EGFR and mTOR inhibitors may help manage Olmsted syndrome symptoms.
8 citations,
December 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Mouse models help understand alopecia areata and find treatments.
June 2023 in “Journal of Biological Chemistry” Get3d protein helps maintain photosynthesis in plants and photosynthetic bacteria.
 2 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
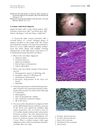
2 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A 65-year-old woman has a growing bald spot on her scalp.
 68 citations,
December 2014 in “Cell Biochemistry and Function”
68 citations,
December 2014 in “Cell Biochemistry and Function” Nuclear hormone receptors play a significant role in skin wound healing and could lead to better treatment methods.
 36 citations,
September 2009 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine”
36 citations,
September 2009 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine” New treatments targeting skin stem cells show promise for skin repair, anti-aging, and cancer therapy.
 17 citations,
October 2017 in “Scientific reports”
17 citations,
October 2017 in “Scientific reports” Fine wool sheep have more genes for wool quality, while coarse wool sheep have more for skin and muscle traits.
 3 citations,
September 2005 in “Experimental dermatology”
3 citations,
September 2005 in “Experimental dermatology” The cornified envelope is crucial for skin's barrier function and involves key proteins and genetic factors.
 2 citations,
July 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
2 citations,
July 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Autophagy changes the protein makeup of hair.
 57 citations,
July 2005 in “Genetics”
57 citations,
July 2005 in “Genetics” Key genes are crucial for Drosophila wing development and could be insecticide targets.
71 citations,
May 2006 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” TTD hair brittleness is caused by multiple structural abnormalities.
 66 citations,
June 2010 in “Experimental Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2010 in “Experimental Dermatology” The hair follicle is a great model for research to improve hair growth treatments.
 November 2023 in “Frontiers in cell and developmental biology”
November 2023 in “Frontiers in cell and developmental biology” Hair aging is caused by stress, hormones, inflammation, and DNA damage affecting hair growth and color.
 September 2023 in “Nature communications”
September 2023 in “Nature communications” Alk1 in specific cells is crucial for proper nerve branching and hair function.
 33 citations,
June 2017 in “Developmental Biology”
33 citations,
June 2017 in “Developmental Biology” Mice can correct hair follicle orientation without certain genes, but proper overall alignment needs those genes.
 15 citations,
February 1999 in “The anatomical record”
15 citations,
February 1999 in “The anatomical record” Some mutant mice have hair with abnormal cross-linking, mainly in the cuticle, not affecting other hair parts.
 5 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology”
5 citations,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology” Hair strength is similar across different scalp areas, and not affected by age, gender, or hair thickness.
1 citations,
November 2023 in “Cosmetics” Surfactants damage hair, but sealing the cuticle can prevent this.
22 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics” Understanding intermediate filaments helps explain hair health and related diseases.
 10 citations,
May 2018 in “Forensic Science International”
10 citations,
May 2018 in “Forensic Science International” Shrunken heads retain some facial features and hair characteristics, allowing for limited individual identification.
 1 citations,
November 2022 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)”
1 citations,
November 2022 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Male and female human hairs have different microscopic structures that can help in forensic analysis.
186 citations,
December 2012 in “Current opinion in cell biology” Keratin proteins are increasingly recognized as important for cell health and are linked to many diseases.
 207 citations,
March 2012 in “Development”
207 citations,
March 2012 in “Development” Skin needs dermal β-catenin activity for hair growth and skin cell multiplication.
 9 citations,
November 2019 in “Cell calcium”
9 citations,
November 2019 in “Cell calcium” The STIM1 R304W mutation in mice leads to bone changes and teeth hair growth.
 7 citations,
November 2013 in “Pediatric and Developmental Pathology”
7 citations,
November 2013 in “Pediatric and Developmental Pathology” Over half of the children had abnormal hair under a microscope, with many having genetic hair conditions.
 159 citations,
July 2006 in “Endocrine Reviews”
159 citations,
July 2006 in “Endocrine Reviews” Estrogens significantly influence hair growth by interacting with receptors in hair follicles and may help regulate the hair growth cycle.
 81 citations,
April 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
81 citations,
April 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair shedding is an active process that could be targeted to treat hair loss.
 66 citations,
August 2001 in “Experimental Dermatology”
66 citations,
August 2001 in “Experimental Dermatology” Human hair follicle cells can grow hair when put into mouse skin if they stay in contact with mouse cells.
 52 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
52 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The document concludes that mouse models are crucial for studying hair biology and that all mutant mice may have hair growth abnormalities that require detailed analysis to identify.
 15 citations,
July 2004 in “Journal of morphology”
15 citations,
July 2004 in “Journal of morphology” Monotreme hair structure and protein distribution are similar to other mammals, but their inner root sheath cornifies differently, suggesting a unique evolution from reptile skin.
























