 10 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry”
10 citations,
July 2022 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry” Adding a second method to PROTACs could improve cancer treatment.
March 2019 in “SLAS TECHNOLOGY” New technologies show promise in healing wounds, treating cancer, autoimmune diseases, and genetic disorders.
73 citations,
November 2001 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Markers help differentiate between apocrine and eccrine sweat glands to identify sweat gland tumors.
5 citations,
July 2022 in “Genes” Increasing EGR1 levels makes hair root cells grow faster.
 30 citations,
August 2010 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
30 citations,
August 2010 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Cetuximab can cause eyelash growth, which is rare but manageable.
 10 citations,
May 2012 in “PloS one”
10 citations,
May 2012 in “PloS one” Low ERCC3 gene activity is linked to non-pigmented hair growth.
 8 citations,
May 2004 in “Textile Research Journal”
8 citations,
May 2004 in “Textile Research Journal” Scientists made antibodies to tell cashmere and wool apart, which could improve how we identify animal fibers.
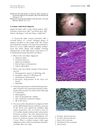 2 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A 65-year-old woman has a growing bald spot on her scalp.
 June 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2023 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Coinheritance of BRCA2 and CYLD genes may lead to new treatment options for certain cancers.
 May 2017 in “American Society of Health-System Pharmacists eBooks”
May 2017 in “American Society of Health-System Pharmacists eBooks”  411 citations,
April 2010 in “Gastroenterology”
411 citations,
April 2010 in “Gastroenterology” Targeting colon cancer stem cells might lead to better treatment results.
 185 citations,
December 2011 in “Molecular and cellular endocrinology”
185 citations,
December 2011 in “Molecular and cellular endocrinology” Skin cells produce and activate vitamin D, which regulates skin functions and supports hair growth.
 141 citations,
September 2016 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
141 citations,
September 2016 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Taxane chemotherapy can cause skin, hair, and nail side effects, which are often under-reported and can affect patient quality of life.
 130 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
130 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Estrogen Receptor ß (ERß) is the main hormone controller in human skin and hair follicles, not Estrogen Receptor α (ERα) or the Androgen Receptor (AR).
 129 citations,
January 2007 in “Otology & Neurotology”
129 citations,
January 2007 in “Otology & Neurotology” Gene therapy with the Math1 gene helped regenerate balance-related cells and improve balance in mice.
 69 citations,
January 2013 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
69 citations,
January 2013 in “Frontiers in Immunology” The FOXN1 gene is crucial for developing immune cells and preventing immune disorders.
 68 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
68 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Acne is caused by genetics, diet, hormones, and bacteria, with treatments not yet curative.
 39 citations,
October 2015 in “Case Reports”
39 citations,
October 2015 in “Case Reports” Some people experience severe, long-lasting side effects from fluoroquinolone antibiotics, leading to the recommendation of limited use and increased awareness of these risks.
 24 citations,
September 2005 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry”
24 citations,
September 2005 in “Journal of Cellular Biochemistry” Retinoids increase steroid sulfatase activity in leukemia cells through RARα/RXR and involves certain pathways like phosphoinositide 3-kinase and ERK-MAP kinase.
 18 citations,
June 2009 in “Journal of Molecular Endocrinology”
18 citations,
June 2009 in “Journal of Molecular Endocrinology” Finasteride exposure harms tadpole reproduction and hormone balance.
 14 citations,
February 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
14 citations,
February 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Immune checkpoint inhibitors can cause skin issues but are linked to better cancer outcomes.
 14 citations,
April 2014 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
14 citations,
April 2014 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Acne is caused by multiple factors including oil production, bacteria, inflammation, and possibly diet and environment.
 12 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
12 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Low-Level Laser Therapy and other light treatments for hair growth lack strong evidence and need more research.
 11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Skin reactions to drugs are common and can be deadly, usually requiring stopping the drug and may be better prevented with genetic testing in the future.
 9 citations,
November 2020 in “Medical Hypotheses”
9 citations,
November 2020 in “Medical Hypotheses” Hair loss may link to weaker COVID-19 immunity, suggesting possible need for extra vaccine boost.
 9 citations,
January 2005 in “Experimental dermatology”
9 citations,
January 2005 in “Experimental dermatology” Melatonin receptors in hair follicles help regulate hair growth and could treat hair loss.
 8 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
8 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Caffeine improves hair growth, thickness, and reduces shedding.
 8 citations,
June 2019 in “Scientific Reports”
8 citations,
June 2019 in “Scientific Reports” Increased PPARGC1α relates to hair thinning in common baldness.
 6 citations,
December 2017 in “Molecular Medicine Reports”
6 citations,
December 2017 in “Molecular Medicine Reports” Wnt5a may contribute to psoriasis by reducing skin cell growth, blocking skin cell maturation, and increasing inflammation.
 6 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
6 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Chicken feather gene mutation helps understand human hair disorders.



























