January 2016 in “Indian dermatology online journal” Frontal fibrosing alopecia causes hair loss at the front hairline, and no effective treatment exists.
 July 2015 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
July 2015 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” A 66-year-old woman experienced hair loss due to Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, a condition with no consistently effective treatment, but it usually stabilizes over time. More research is needed for better understanding and treatment options.
A 73-year-old woman's unusual hair loss and growth led to the discovery of a rare condition causing too much testosterone, which improved after her ovaries were removed.
 18 citations,
November 2012 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
18 citations,
November 2012 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” A 66-year-old man with a rare case of male frontal fibrosing alopecia did not regrow hair despite treatment.
14 citations,
February 2013 in “PubMed” Patients treated with long-term intralesional corticosteroids for alopecia areata should be monitored for bone density changes and advised on osteoporosis prevention.
 8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The review suggests there's no agreed treatment for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, but hydroxychloroquine and 5a-reductase inhibitors are most effective. New treatments like platelet-rich plasma and LED light could help if standard treatments fail.
 April 2023 in “Our Dermatology Online”
April 2023 in “Our Dermatology Online” Trichoscopy is effective in diagnosing trichotillomania by showing specific hair patterns.
January 2020 in “International Journal of Trichology” Androgen-producing ovarian tumors can cause male-pattern hair loss in women.
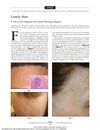 63 citations,
October 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
63 citations,
October 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Isolated long hairs at the original hairline can help diagnose Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia.
 October 2024 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
October 2024 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” Leydig cell tumors can cause high testosterone and symptoms like hair loss in postmenopausal women, but surgery can improve these symptoms.
Early diagnosis and treatment of frontal fibrosing alopecia are crucial to prevent permanent hair loss.
 2 citations,
August 2011 in “Revista Medica De Chile”
2 citations,
August 2011 in “Revista Medica De Chile” A postmenopausal woman's high testosterone levels and symptoms improved after removing a tumor from her ovary.
 January 2013 in “Revista Clínica Española”
January 2013 in “Revista Clínica Española” A postmenopausal woman's increased male hormone levels were successfully treated with surgery.
 10 citations,
April 2018 in “Maturitas”
10 citations,
April 2018 in “Maturitas” Excess male hormones in postmenopausal women can cause health issues and increase the risk of heart disease and diabetes; treatment depends on the cause.
 October 2024 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
October 2024 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” Leydig cell tumors can cause high testosterone and symptoms in postmenopausal women, and removing them improves symptoms.
May 2024 in “Journal of Fungi” Tinea capitis in adults, especially postmenopausal Black women, needs prompt treatment with oral antifungals to avoid scarring.
July 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dentistry” A 46-year-old man showed symptoms of a rare condition usually seen in postmenopausal women, highlighting the need for dentist-dermatologist collaboration.
 January 2003 in “Humana Press eBooks”
January 2003 in “Humana Press eBooks” Dihydrotestosterone and 5α-Reductase play a role in hair loss and prostate health, and finasteride can increase hair growth in men without affecting sperm production, but it doesn't work for postmenopausal women with hair loss.

The authors suggest that 5-α-reductase inhibitors, like dutasteride, are effective in treating frontal fibrosing alopecia and should be the first-line treatment, with other options for severe cases. They also recommend further research on Janus kinase inhibitors.
 September 2023 in “Gynäkologische Endokrinologie”
September 2023 in “Gynäkologische Endokrinologie” Menopause causes skin and hair to become drier and thinner, but hormone therapy can improve these conditions.
 2 citations,
October 2015 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
2 citations,
October 2015 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” The woman's surgery lowered her testosterone and improved scalp hair loss but did not change her excessive body hair.

A rare case of a woman having both lichen planus pigmentosus and classic lichen planopilaris at the same time.
 January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” A woman's hair loss was linked to a rare hormone-secreting ovarian tumor, treated with surgery and hair loss medication.
 January 2007 in “Inpharma Weekly”
January 2007 in “Inpharma Weekly” Dutasteride is more effective for male pattern baldness than finasteride, and black cohosh extract BNO 1055 is as effective as conjugated estrogens in treating postmenopausal symptoms, with added benefits in reducing sweating and mental symptoms.
 21 citations,
December 2012 in “Maturitas”
21 citations,
December 2012 in “Maturitas” Testosterone implants in women require pharmacological dosing to be effective and are generally safe and well-tolerated.
 5 citations,
June 2004 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society”
5 citations,
June 2004 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society” Testosterone therapy can improve sexual satisfaction and mood in surgically menopausal women when used with estrogen, but its long-term safety and effects on naturally menopausal and premenopausal women are unclear.
 May 2019 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
May 2019 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” The conclusion is that managing hair loss conditions like FFA and melanoma requires individualized approaches, considering new findings and balancing treatment benefits with potential risks.
 June 2017 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)”
June 2017 in “DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals)” Using GnRHa agonists helps diagnose and treat ovarian hyperthecosis when surgery isn't possible.
 26 citations,
February 2009 in “Drug Development Research”
26 citations,
February 2009 in “Drug Development Research” 17α-estradiol is a safe estrogen that might protect the brain and doesn't cause feminization, needing more research for treating brain diseases.
 20 citations,
April 2006 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
20 citations,
April 2006 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Antiandrogen therapies are beneficial for treating skin and hair conditions related to androgen levels.























