 20 citations,
March 2023 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
20 citations,
March 2023 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Baricitinib improved severe hair loss in adults over 52 weeks and was safe to use.
 48 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
48 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib 2% ointment helped hair regrow in 3 out of 10 patients with alopecia areata, but caused side effects like scalp irritation and raised cholesterol in some.
 16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
16 citations,
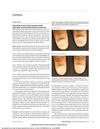
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” A patient with complete hair loss regrew all her hair using tofacitinib.
 6 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
6 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Upadacitinib improved hair regrowth and quality of life in alopecia areata patients with minimal side effects.
 41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib citrate improved nail dystrophy and pain in patients with alopecia universalis without causing side effects.
 9 citations,
January 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
9 citations,
January 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” A 14-year-old girl with severe hair loss regrew her hair using upadacitinib.
 196 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight”
196 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight” Ruxolitinib effectively regrows hair in most patients with severe hair loss.
 2 citations,
December 2022 in “PNAS nexus”
2 citations,
December 2022 in “PNAS nexus” SCD-153 shows promise as an effective topical treatment for alopecia areata.
13 citations,
February 2017 in “Clinical rheumatology” Tofacitinib may help treat nail dystrophy, especially when other treatments fail.
55 citations,
October 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” The review suggests that other immune cells besides CD8+ T cells may contribute to alopecia areata and that targeting regulatory cell defects could improve treatment.
 1 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
1 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Platelet-rich plasma can increase hair density and may help treat some skin conditions, but it's costly, not FDA-approved, and needs more research.
 May 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Treg cell-based therapies might help treat hair loss from alopecia areata, but more research is needed to confirm safety and effectiveness.
July 2024 in “European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry” New small molecule drugs could help treat hair loss.

Hair loss can be caused by hormones, illness, autoimmune disorders, or vitamin deficiencies, and treatments vary depending on the type.
 September 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
September 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” Ritlecitinib effectively improves hair growth in alopecia areata patients, regardless of hair loss pattern.
19 citations,
August 2019 in “Dermatologic therapy” Janus kinase inhibitors show promise for treating alopecia areata but need more research for confirmation.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” Different causes of beard hair loss have various treatments, including medications, lifestyle changes, and procedures to stimulate hair growth.
 20 citations,
January 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
20 citations,
January 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Recent advances in hair loss treatments show significant progress.
 November 2023 in “Aktualʹnì problemi sučasnoï medicini”
November 2023 in “Aktualʹnì problemi sučasnoï medicini” The guidelines suggest using various treatments, including antidepressants and steroids, for alopecia areata and discuss the condition's genetic and immune aspects.
 1 citations,
January 2020 in “Surgical & Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2020 in “Surgical & Cosmetic Dermatology” Combining oral minoxidil with JAK inhibitors helps regrow hair in severe alopecia areata cases.
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Combination therapies might work better for some vitiligo patients, but results vary.
 January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology”
January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia, a common hair loss condition, can be treated with topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, or oral spironolactone, and new treatments like platelet-rich plasma, low-level laser therapy, and janus-kinase inhibitors are being explored.
 May 2023 in “Elsevier eBooks”
May 2023 in “Elsevier eBooks” Systemic immunotherapies are used for immune-related hair loss but not usually for genetic hair loss, unless the patient has both conditions.
 20 citations,
January 2018 in “Expert opinion on emerging drugs”
20 citations,
January 2018 in “Expert opinion on emerging drugs” JAK inhibitors may soon be a safe and effective treatment for alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
November 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
2 citations,
November 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Oral tofacitinib can treat both psoriasis and alopecia universalis by normalizing inflammatory pathways.
 17 citations,
August 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
17 citations,
August 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” The document concludes that oral finasteride and topical minoxidil are effective for genetic hair loss, while other treatments for different types of hair loss show promise but need more research.
 October 2020 in “Revista médica sinergía/Revista médica sinergia”
October 2020 in “Revista médica sinergía/Revista médica sinergia” Alopecia areata is a complex condition causing hair loss, linked to genetics and immune system issues, and may be related to other autoimmune diseases; treatments vary in effectiveness.
 12 citations,
December 2022 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
12 citations,
December 2022 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” New oral treatments for adult hair loss show promise, especially JAK inhibitors, with mild side effects.
 February 2024 in “PloS one”
February 2024 in “PloS one” Tofacitinib and adalimumab are promising treatments for cicatricial alopecia with few side effects.
January 2018 in “Figshare” Ruxolitinib and tofacitinib are effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.
























