 24 citations,
September 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy”
24 citations,
September 2020 in “Dermatology and therapy” Oral minoxidil 5 mg daily increases hair growth safely in men with hair loss, with minor side effects.
 38 citations,
March 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs”
38 citations,
March 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs” Bimatoprost is promising for treating some types of hair loss but needs more testing for androgenetic alopecia.
 9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology”
9 citations,
December 2017 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” New targeted therapies for hair loss from alopecia areata show promise, with personalized treatment expected in the future.
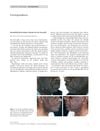 6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Oral minoxidil can cause inflamed, ingrown hairs in the beard area.
 January 2016 in “Chemistry & Industry”
January 2016 in “Chemistry & Industry” Two drugs, tofacitinib and ruxolitinib, may help regrow hair by activating hair follicles.
 September 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports”
September 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports” A man got heart and swelling issues from a hair loss medication, so doctors advise careful use, especially in people with past health problems.
 5 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
5 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil is an effective and safe treatment for hair loss.
 1 citations,
October 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
1 citations,
October 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” Some treatments for severe hair loss work but often have side effects, with baricitinib showing the most promise.
 40 citations,
September 2017 in “F1000Research”
40 citations,
September 2017 in “F1000Research” Oral minoxidil effectively reduces hair shedding in women with CTE, with no major side effects.
 34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” Some treatments work for common baldness, but there's less evidence for other hair loss types, and more research is needed.
Many hair loss myths lack strong evidence, but some treatments are proven to work.
138 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Ritlecitinib and brepocitinib effectively regrow hair in alopecia areata patients.
20 citations,
December 2021 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Continuous treatment with ritlecitinib and brepocitinib is needed to maintain hair regrowth in alopecia areata.
 14 citations,
August 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
14 citations,
August 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Low-dose oral minoxidil is a safe treatment for hair loss, with the main side effect being excessive hair growth. Other side effects like foot swelling, low blood pressure when standing, and heart rate changes are rare.
 February 2024 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
February 2024 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Dermatologists recommend oral dutasteride for male hair loss, low-dose oral minoxidil for female hair loss, and a multidisciplinary approach for young patients, with caution during pregnancy.
 6 citations,
March 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Medicine”
6 citations,
March 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Medicine” Finasteride microspheres help reduce hair loss for up to eight weeks with fewer side effects.
 May 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology”
May 2023 in “International Journal of Trichology” Low-dose oral Minoxidil is an effective treatment for hair loss with minimal serious side effects.
 39 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil safely treats hair loss, with hypertrichosis as main side effect.
 36 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
36 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Oral minoxidil helps hair growth, is cost-effective, and mostly well-tolerated.
 6 citations,
June 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology”
6 citations,
June 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology” Finasteride works for hair loss by maintaining existing hair follicles, not reversing miniaturization.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” The new delivery system improves treatment for hair loss by enhancing drug absorption and effectiveness.
 33 citations,
January 2016 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
33 citations,
January 2016 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Taking 1 mg of finasteride daily can increase hair count and improve hair appearance, but it may have side effects on sexual function and a potential risk of prostate cancer. It may not be effective for postmenopausal women unless taken in higher doses.
 1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical research in dermatology” Hair loss, known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is often caused by hormones and can be diagnosed using noninvasive techniques. Treatments include topical minoxidil and oral finasteride, with new treatments being explored. There may also be a link between this type of hair loss and heart disease risk.
 60 citations,
October 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology”
60 citations,
October 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology” Zinc can both inhibit and stimulate mouse hair growth, and might help recover hair after chemotherapy.
 25 citations,
July 2017 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
25 citations,
July 2017 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Herbal products might promote hair growth with fewer side effects, but more research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
 52 citations,
June 1999 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America”
52 citations,
June 1999 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America” Antiandrogen treatments combined with oral contraceptives can help manage hair growth and hair loss in women with PCOS.
 7 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” JAK inhibitors offer new hope for treating severe alopecia areata.
 31 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
31 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Minoxidil helps stabilize hair loss, increase density, and reduce shedding after hair transplant surgery.
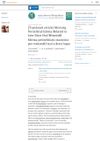 April 2023 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
April 2023 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Low doses of oral minoxidil, a hair loss treatment, can cause temporary morning swelling around the eyes, but it's not serious and can disappear with continued use or dose adjustment.
 April 2021 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery”
April 2021 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery” Hair restoration can be achieved through non-surgical treatments like minoxidil, antiandrogens, phototherapy, and PRP procedures, or through surgical methods like hair transplantation. Continued treatment is needed to maintain results, and full results are visible after 12-18 months.


























