 April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Stress in hair follicle cells increases certain immune-related proteins, which might contribute to hair loss conditions.
[object Object] 52 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Apremilast may help treat hair loss in alopecia areata.
25 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” New treatments for alopecia areata may target specific immune cells and pathways involved in hair loss.
6 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia areata involves complex immune and genetic factors, with potential treatment targets identified, but more research is needed.
1 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Vδ1+ T-cells in the skin contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata and could be targeted for treatment.
 April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Too much IKZF1 and Ikaros protein may cause alopecia areata.
717 citations,
June 2010 in “Nature” Alopecia areata involves both innate and adaptive immunity, with specific genes linked to the disease.
 January 2016 in “Human & Experimental Toxicology”
January 2016 in “Human & Experimental Toxicology” A specific DNA sequence caused hair loss in male mice by activating immune cells and increasing a certain immune signal.
701 citations,
August 2014 in “Nature medicine” Alopecia areata can be reversed by JAK inhibitors, promoting hair regrowth.
 March 2018 in “Suez Canal University Medical Journal”
March 2018 in “Suez Canal University Medical Journal” NKG2D gene polymorphism doesn't affect SLE risk but may influence symptoms like rash and hair loss.
 82 citations,
March 2016 in “Autoimmunity reviews”
82 citations,
March 2016 in “Autoimmunity reviews” Animal models have helped understand hair loss from alopecia areata and find new treatments.
 June 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
June 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” ILC1-like cells can cause alopecia areata by attacking hair follicles.

Innate lymphoid cells type 1 may contribute to alopecia areata by damaging hair follicles.
ILC1-like cells can independently cause alopecia areata by affecting hair follicles.
15 citations,
December 2018 in “International journal of environmental research and public health/International journal of environmental research and public health” EGCG may help treat alopecia areata by blocking certain immune responses and reducing specific harmful immune cells.
 15 citations,
May 2016 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
15 citations,
May 2016 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” ULBP3 could be a marker for diagnosing alopecia areata incognita and may be linked to its cause and development.
 March 2022 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
March 2022 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” ULBP3 levels are higher in Tinea capitis patients and may help predict the disease's severity.
[object Object]  148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing patchy hair loss, often with other autoimmune disorders, but its exact causes are unknown.
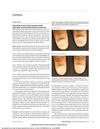 41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib citrate improved nail dystrophy and pain in patients with alopecia universalis without causing side effects.
 12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics”
12 citations,
May 2017 in “Pharmacology & therapeutics” Targeting immune tolerance issues in Alopecia Areata could restore hair growth and maintain remission.
 3 citations,
June 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
3 citations,
June 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Oxidative stress may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata and antioxidants could potentially help as a treatment.
 April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal”
April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, linked to genetic factors and immune system issues, with no cure yet.
 55 citations,
April 2010 in “Cancer and Metastasis Reviews”
55 citations,
April 2010 in “Cancer and Metastasis Reviews” TGFβ's manipulation of inflammation and immune cells affects cancer spread, suggesting new treatment strategies and biomarkers.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” Understanding the immune-related causes of Alopecia Areata has led to potential treatments like JAK inhibitors.

Wild African goats have genetic adaptations for surviving harsh desert conditions.
 341 citations,
November 2009 in “The FASEB Journal”
341 citations,
November 2009 in “The FASEB Journal” Calreticulin has roles in healing, immune response, and disease beyond its known functions in the endoplasmic reticulum.
 306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The skin has a complex immune system that is essential for protection and healing, requiring more research for better wound treatment.
 290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, stress, and diet, and may be prevented by a high soy oil diet.
 222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight”
222 citations,
September 2016 in “JCI insight” Tofacitinib is safe and effective for severe alopecia areata, but hair loss may return 2 months after stopping treatment.
 185 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
185 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A man with severe hair loss and skin disease regrew his hair with no side effects after taking tofacitinib.






















