1 citations,
August 2019 in “Journal of pediatric & adolescent gynecology” A new genetic change causing early stop in the androgen receptor gene was found in a patient with androgen insensitivity syndrome.
1 citations,
January 2018 in “Indian dermatology online journal” Early diagnosis and genetic evaluation of ADULT syndrome are crucial to reduce stress and medical costs.
1 citations,
May 2024 in “Applied Sciences” Cordyceps militaris is a promising, cost-effective medicinal fungus with health benefits and efficient production methods.

Genetic testing can help diagnose skin conditions but needs more research for full effectiveness.
 October 2023 in “IJEM case reports”
October 2023 in “IJEM case reports” A 15-year-old girl with no menstrual period was diagnosed with a genetic condition that makes her body unable to respond to male hormones, leading to female characteristics despite having male genetic makeup.
 September 2023 in “Cutis”
September 2023 in “Cutis” A baby girl has a hair disorder called monilethrix, causing fragile hair that may improve over time.

Inhibiting AP-1 changes skin tumor types and affects tumor cell identity.

Inhibiting AP-1 changes skin tumor types and affects tumor cell identity.
Moles may stop growing due to cell cooperation, not just because of individual cell aging.
 November 2018 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice”
November 2018 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice” Using old drugs for new uses can help treat rare immune deficiencies.
 May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” The first Japanese family with Marie Unna hereditary hypotrichosis showed hair condition improvement in a child and highlighted the risk of misdiagnosis.
January 2018 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” A child with Olmsted syndrome showed mild improvement in hair and skin issues with treatment.
July 2016 in “Cancer research” Mutant cells in hair follicles are influenced by their location and interactions with surrounding cells.
 January 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
January 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Some cells may slow melanoma growth, a protein could affect skin pigmentation, a gene-silencing method might treat hair defects, skin bacteria changes likely result from eczema, and a defensin protein could help treat multiple sclerosis.
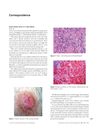 October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
October 2010 in “International Journal of Dermatology” An 86-year-old man with prostate cancer was diagnosed with a rare, low-grade breast cancer and underwent surgery but declined additional hormone therapy.
 November 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric Nursing”
November 2009 in “Journal of Pediatric Nursing” Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a common genetic disorder that can cause a range of symptoms and requires personalized treatment.
 July 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2004 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis and treatment are crucial in dermatology, and it presents various findings on skin conditions and treatments.
 January 2000 in “BioScience”
January 2000 in “BioScience” The document concludes that understanding hair biology is key to treating hair disorders, with gene therapy showing potential as a future treatment.
 March 2013 in “Journal of pediatric nursing”
March 2013 in “Journal of pediatric nursing” The case emphasizes the need for careful screening in children for insulin resistance and related conditions.
September 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” 5% topical minoxidil improves hair density and quality in monilethrix patients.
June 2022 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Oral minoxidil and growth factors improved hair density and thickness in a girl with hereditary hair loss.
58 citations,
November 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The Foxn1 gene is essential for normal nail and hair development.
29 citations,
October 2019 in “Journal of dermatological science” Studying premature aging syndromes helps understand human aging and suggests potential treatments.
12 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in dermatology” The mouse model could be useful for baldness research and testing treatments like testosterone, cyproterone acetate, and minoxidil.
 5 citations,
November 2021 in “Saudi medical journal”
5 citations,
November 2021 in “Saudi medical journal” The document reports three sisters with Woodhouse-Sakati syndrome showing typical symptoms and unusual gynecological anomalies.
 December 2024 in “Frontiers in Genetics”
December 2024 in “Frontiers in Genetics” EGFR and mTOR inhibitors may help manage Olmsted syndrome symptoms.
 July 2023 in “Developmental medicine and child neurology/Developmental medicine & child neurology”
July 2023 in “Developmental medicine and child neurology/Developmental medicine & child neurology” DFMO treatment improves hair growth, muscle tone, and development in Bachmann-Bupp syndrome patients.
 April 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
April 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Gene therapy with a vitamin D receptor gene improved hair growth in rats with a type of rickets-related baldness.
 June 2017 in “Journal of clinical and investigative dermatology”
June 2017 in “Journal of clinical and investigative dermatology” Red blood cell folate levels are reliable indicators of long-term folate status in alopecia areata patients.
 January 2023 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2023 in “Springer eBooks” Epidermolysis bullosa is an inherited condition causing fragile skin with no cure, managed by wound care and experimental treatments show promise.


















