Topical minoxidil can help regrow hair in people with common baldness.
February 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil helps increase hair density in traction alopecia.
[object Object] November 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Minoxidil and PRP can help convert miniaturized hair follicles back to normal in male pattern baldness.
November 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Topical minoxidil 5% is better for treating female pattern hair loss than topical sildenafil 1%.
October 2021 in “QJM: An International Journal of Medicine” Both sildenafil and minoxidil effectively treat male hair loss, but impact hair differently.
 February 2019 in “Case medical research”
February 2019 in “Case medical research” Using lasers to deliver minoxidil can potentially improve its effectiveness in treating male pattern hair loss.
 152 citations,
April 2012 in “Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery”
152 citations,
April 2012 in “Recent Patents on Inflammation & Allergy Drug Discovery” Minoxidil treats hair loss, promotes growth, has side effects, and has recent patents.
 36 citations,
May 2015 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
36 citations,
May 2015 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Low dose oral minoxidil helps regrow hair in permanent chemotherapy-induced alopecia.
 31 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
31 citations,
October 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Minoxidil helps stabilize hair loss, increase density, and reduce shedding after hair transplant surgery.
 20 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
20 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in Clouston's syndrome improved with minoxidil and tretinoin treatment.
 18 citations,
March 2014 in “Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy”
18 citations,
March 2014 in “Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy” New gel formulas without ethanol and propylene glycol, containing a minoxidil-methyl-β-cyclodextrin complex, have been created for treating hair loss.
 17 citations,
October 2013 in “F1000Research”
17 citations,
October 2013 in “F1000Research” A 2-year-old boy grew excessive hair after using minoxidil for hair loss, but it improved when the treatment stopped.
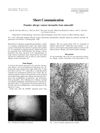 17 citations,
May 1998 in “Contact Dermatitis”
17 citations,
May 1998 in “Contact Dermatitis” Minoxidil can cause pustular allergic reactions on skin.
 14 citations,
July 1987 in “Contact Dermatitis”
14 citations,
July 1987 in “Contact Dermatitis” Minoxidil can cause allergic skin reactions in some users.
 1 citations,
April 2022 in “JAAD case reports”
1 citations,
April 2022 in “JAAD case reports” Oral minoxidil helped significantly regrow hair in a patient with traction alopecia.
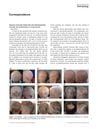 1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl with alopecia universalis regrew most of her hair after treatment with simvastatin/ezetimibe, minoxidil, and prednisolone.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Oral minoxidil can potentially increase hair growth in people suffering from Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia.
 1 citations,
August 1995 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood”
1 citations,
August 1995 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood” Minoxidil helped a boy regrow his hair after intense chemotherapy for leukaemia.
[object Object]  November 2024 in “Skin Health and Disease”
November 2024 in “Skin Health and Disease” Minoxidil is effective for promoting hair growth and has various dermatological uses.
 April 2024 in “JAMA dermatology”
April 2024 in “JAMA dermatology” Oral minoxidil is as effective as topical minoxidil for male hair loss but has more side effects like excessive hair growth and headaches.
 April 2024 in “MRIMS journal of health sciences”
April 2024 in “MRIMS journal of health sciences” Using growth factor injections and minoxidil together can significantly improve hair growth in people with hair loss.
 January 2024 in “Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy”
January 2024 in “Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy” Using minoxidil with laser therapy is more effective for female hair loss than minoxidil alone.
 May 2023 in “JAAD international”
May 2023 in “JAAD international” Minoxidil-dutasteride tattooing can potentially help regrow hair, especially in men who already have some thin hair.
 May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Oral minoxidil improved male baldness, but had side effects; certain antibiotics effectively treated a rare scalp condition; hair transplants might trigger another scalp condition.
The document concludes that current hair loss treatments have limitations and suggests researching new treatments targeting different factors of hair loss.
 5 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
5 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil is an effective and safe treatment for hair loss.
 April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Low-intensity ultrasound may protect hair follicles from damage caused by a common chemotherapy drug.
 2 citations,
January 2019 in “Case Reports in Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2019 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” A 66-year-old woman's thick scalp and hair loss were confirmed as lipedematous alopecia, a rare condition possibly influenced by genetics, with no effective treatment known.
 2 citations,
September 2022 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas”
2 citations,
September 2022 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” For sensitive scalp, treatment is personalized and may include specific medications and hydration, while avoiding stress and irritating products.
 March 2024 in “Facial plastic surgery clinics of North America”
March 2024 in “Facial plastic surgery clinics of North America” Finasteride and minoxidil are approved treatments for hair loss, and hair transplants can be effective but require careful patient selection.























