 7 citations,
February 2022 in “JAAD International”
7 citations,
February 2022 in “JAAD International” COVID-19 may be linked to hair loss or worsening of hair loss in some people.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Pakistan Medical Association”
April 2023 in “Journal of Pakistan Medical Association” Baricitinib is effective in promoting hair growth in severe alopecia areata.
New treatments for alopecia areata, like JAK inhibitors and immunomodulators, are promising.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Gender affects hair and scalp characteristics, with differences in hormone responses, graying patterns, and trace metals.
 October 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
October 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Targeted immunotherapy could be a promising new treatment for hair regrowth.
 15 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” The document concludes that understanding and treatments for alopecia areata have significantly advanced, now recognizing it as an autoimmune disorder.
 April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The study suggests that changes in immune system receptors and their interaction with a cell component may be important in the development of a type of hair loss condition.
 October 2020 in “Revista médica sinergía/Revista médica sinergia”
October 2020 in “Revista médica sinergía/Revista médica sinergia” Alopecia areata is a complex condition causing hair loss, linked to genetics and immune system issues, and may be related to other autoimmune diseases; treatments vary in effectiveness.
 92 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
92 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” All-trans retinoic acid causes hair loss by increasing TGF-β2 in hair follicle cells.
 35 citations,
January 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
35 citations,
January 1993 in “International Journal of Dermatology” People with HIV and low T cell counts have more hair and scalp problems.
 48 citations,
July 1992 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
48 citations,
July 1992 in “International Journal of Dermatology” HIV can cause various nail and hair disorders, important for early diagnosis and treatment.
55 citations,
April 2015 in “BMC medicine” Stem Cell Educator therapy helps regrow hair and improve life quality in alopecia areata patients.
 September 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
September 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Lower vitamin D levels are linked to higher CRP levels in people with a type of hair loss called alopecia areata.
 7 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of comparative pathology”
7 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of comparative pathology” CD8+ T cells play a key role in graft-versus-host disease in certain mice models.
June 2022 in “Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology” A woman's shingles infection triggered her first episode of a rare neurological disorder and blood vessel inflammation.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Eating grape powder may reduce the severity of skin allergy symptoms.
 January 2025 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
January 2025 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Hair follicles are key to treating vitiligo and alopecia areata, but challenges exist.
 2 citations,
April 2024 in “Advanced Materials”
2 citations,
April 2024 in “Advanced Materials” A microneedle patch can help regrow hair by restoring immune balance in hair follicles.
 January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” The conference highlighted new diagnostic tools, the role of genetics in hair loss, and emerging treatments.
 101 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
101 citations,
January 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Nerves and chemicals in the body can affect hair growth and loss.
 August 2024 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
August 2024 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Hypothyroidism may cause certain types of hair loss.
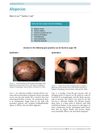 February 2013 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice”
February 2013 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice” Different types of alopecia in children require specific diagnoses and treatments.
 6 citations,
June 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
June 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” People with alopecia areata have higher levels of RBP4 protein and antibodies against it.

COVID-19 may trigger or worsen rapid hair loss in alopecia areata.
 July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition caused by immune factors and can be treated with JAK inhibitors.
 8 citations,
January 2007 in “Mycoses”
8 citations,
January 2007 in “Mycoses” A man's scalp infection, mistaken for bacterial, was actually a rare fungal infection treated successfully with antifungal medication.
3 citations,
July 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Stress may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata by affecting immune responses and cell death in hair follicles.
50 citations,
May 2021 in “Frontiers in immunology” Certain immune cells contribute to skin autoimmune diseases, and some treatments can reverse hair loss in these conditions.

TLR2 helps control hair growth and regeneration, and its reduction with age or obesity can impair hair growth.
 72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Anti-TNF therapy can cause a unique type of hair loss that may get better with topical treatments without stopping the therapy.

























