 August 2022 in “Revista de la Universidad Industrial de Santander/Salud UIS”
August 2022 in “Revista de la Universidad Industrial de Santander/Salud UIS” Stress-related hair loss was reversed with a special medication.
 49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
April 2000 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Despite progress in treatment, the exact cause of Alopecia areata is still unknown.
 1 citations,
March 2023 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
1 citations,
March 2023 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Current treatments for Alopecia Areata have mixed success, and there's a need for better, more accessible options and support for affected individuals.
 31 citations,
September 2014 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
31 citations,
September 2014 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Anthralin is effective for psoriasis and alopecia with minimal systemic side effects but can irritate the skin.
 84 citations,
March 2010 in “Infectious Disease Clinics of North America”
84 citations,
March 2010 in “Infectious Disease Clinics of North America” The document concludes that rapid identification, isolation, and strict infection control are crucial to manage SARS outbreaks.
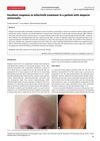 16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
16 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” A patient with complete hair loss regrew all her hair using tofacitinib.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
 October 2023 in “Applied materials today”
October 2023 in “Applied materials today” New treatment for hair loss using special microneedles shows promise in reducing inflammation and promoting hair growth.

People with Down syndrome have a higher risk of skin disorders and need better screening and treatment.
 96 citations,
September 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
96 citations,
September 2021 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Chitosan, a natural substance, can be used to create tiny particles that effectively deliver various types of drugs, but more work is needed to improve stability and control of drug release.
 4 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
4 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Monocytes might be linked to hair loss after COVID-19.
 April 2021 in “HIV & AIDS Review”
April 2021 in “HIV & AIDS Review” Glycyrrhizinic acid spray showed limited effectiveness in treating anogenital warts in HIV patients with low CD4 levels.
 January 2010 in “대한한의학회지”
January 2010 in “대한한의학회지” Yikgeebohyul-tang promotes hair growth and could help treat hair loss.
21 citations,
December 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” T-cells in alopecia areata scalp show abnormal regulation, leading to less inflammation.
 April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” JAK inhibitors help hair growth by boosting beta-catenin activity in hair root cells.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Booster shots of mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 increased protective antibodies without worsening autoimmune skin conditions in patients.
October 2021 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The new aptamer TAGX-0003 shows promise as an effective treatment for hair loss disorder alopecia areata.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Type 1/17 inflammation in psoriasis increases skin cell growth due to a molecule that could be a new treatment target.
12 citations,
April 2017 in “Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine” Patients with severe active alopecia areata have lower CD200 expression and an imbalance in their immune system.
ILC1-like cells may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata.
August 2021 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” TAGX-0003 protected hair follicles and reversed alopecia areata in a mouse model.
 23 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
23 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Apremilast did not work for treating severe alopecia areata.
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” IL-17 and certain immune cells are linked to more severe alopecia areata.
 4 citations,
November 2017 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
4 citations,
November 2017 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Sorafenib may cause hair loss in a way similar to alopecia areata.
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The humanized AA mouse model is better for testing new alopecia areata treatments.
ILC1-like cells may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata and could be new treatment targets.
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Innate lymphoid cells type 1 may contribute to alopecia areata.
7 citations,
December 2016 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” NKG2D+CD4+ T cells are higher in alopecia areata patients and may be involved in the disease.
 1 citations,
June 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
June 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Fetal skin has unique immune cells different from adult skin.
 June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Some multiple sclerosis treatments may trigger hair loss conditions like alopecia areata.




















