 4 citations,
December 2017 in “PubMed”
4 citations,
December 2017 in “PubMed” Minoxidil may help treat hair loss by reducing the activity of a specific enzyme linked to baldness.
21 citations,
June 2011 in “Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science” Hair follicles could help develop eye treatments by studying immune responses.
 10 citations,
November 1997 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
November 1997 in “British Journal of Dermatology” RU58841 significantly increases hair growth rate and initiates more hair cycles, but doesn't affect hair thickness, suggesting it could be a new treatment for baldness.
9 citations,
November 1997 in “British Journal of Dermatology”  6 citations,
January 2021 in “Annals of Dermatology”
6 citations,
January 2021 in “Annals of Dermatology” 650 nm red light helps hair grow and prevents hair loss by affecting certain genes and biological processes.
5 citations,
March 2012 in “PubMed”  16 citations,
September 2018 in “Scientific reports”
16 citations,
September 2018 in “Scientific reports” Scientists created keratinocyte cell lines from human hair that can differentiate similarly to normal skin cells, offering a new way to study skin biology and diseases.
 10 citations,
November 1984 in “Journal of Colloid and Interface Science”
10 citations,
November 1984 in “Journal of Colloid and Interface Science” The study found that the Marangoni effect causes the uneven wetting of surfactant-coated hair due to the surfactant moving into the water.
 2 citations,
December 2016 in “Experimental cell research”
2 citations,
December 2016 in “Experimental cell research” The research found a way to identify and study skin cells with stem cell traits, revealing they behave differently in culture and questioning current stemness assessment methods.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The created skin model with melanoblasts improves the study of skin color and offers an alternative to animal testing.
 September 2013 in “中国医师杂志”
September 2013 in “中国医师杂志” Human scalp hair follicles grow well in Williams E medium, which may help with hair transplants.
 71 citations,
October 2008 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
71 citations,
October 2008 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” HFMs can help study hair growth and test potential hair growth drugs.
 36 citations,
June 2019 in “eLife”
36 citations,
June 2019 in “eLife” The study developed a tool to predict how gut microbes process foods and drugs, showing that similar compounds often share metabolic pathways and effects.
 8 citations,
March 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
8 citations,
March 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Researchers created immortal human skin cells with constant testosterone receptor activity to study hair loss and test treatments.
 3 citations,
December 2000 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
3 citations,
December 2000 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” The study created a new method to test drugs that affect hormone processing in skin.
 27 citations,
June 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
27 citations,
June 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The study found that variations in hair protein genes are likely due to evolutionary deletions or duplications.
25 citations,
March 2002 in “Scanning” Confocal microscopy is better than scanning electron microscopy for studying hair in its natural state and understanding hair products' effects.
 13 citations,
March 2006 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
13 citations,
March 2006 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” The study found that a polymer treatment changes the charge on hair surfaces, making bleached hair smoother and less porous.
 2 citations,
January 1994 in “Journal of S C C J”
2 citations,
January 1994 in “Journal of S C C J” The study concluded that certain hair growth measurements are good indicators of baldness severity and provide a more accurate assessment than subjective grading.
 January 2020 in “International journal of medical parasitology and epidemiology sciences”
January 2020 in “International journal of medical parasitology and epidemiology sciences” The study concluded that itching and scaling on the face may be caused by a Demodex mite infection.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The study created special nanoparticles that effectively deliver an anti-inflammatory drug to treat skin inflammation in psoriasis.
July 2020 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” The study found that minor protein differences between curved and straight Japanese hair are unlikely to significantly affect hair structure.
 100 citations,
September 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
100 citations,
September 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The study found that two enzymes linked to hair loss are located in different parts of the scalp, supporting a common treatment's effectiveness.
 11 citations,
August 2013 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
11 citations,
August 2013 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” The study suggests that a new protease inhibitor can make hair harder to pull out, potentially reducing hair loss.
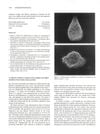 8 citations,
September 1993 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
8 citations,
September 1993 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” A new method helps isolate key hair components to study hair growth and loss.
 7 citations,
June 2017 in “Omics”
7 citations,
June 2017 in “Omics” The study developed a method to analyze ancient hair proteins using very small samples.
6 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of dermatological science” The study found nine new hair protein genes in human hair follicles.
The study identified a key protein involved in producing underarm odor and found ways to inhibit it.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Researchers created human cells that can turn into sebocytes, which may help study and treat skin conditions like acne.
13 citations,
October 2010 in “Methods in molecular biology” Hair follicle culture helps study cell interactions and effects of substances on tissue growth.






















