50 citations,
February 2004 in “Genomics” A gene mutation causes lanceolate hair in rats by disrupting hair shaft integrity.
 October 2023 in “Scientific Reports”
October 2023 in “Scientific Reports” Gene therapy helped rats with a specific type of rickets grow hair without severe inflammation.
 November 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
November 2018 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that specialized hair transplant techniques can be effective, with varying success rates depending on the donor area and patient factors.
4 citations,
May 2014 in “Pharmaceutical Biology” Glycyrrhizic acid from sweet licorice can effectively remove hair without skin irritation.
3 citations,
April 2002 in “Animal Science” Spermidine injections increased wool growth rate in lambs without changing fibre thickness.
 118 citations,
May 2015 in “European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics”
118 citations,
May 2015 in “European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics” The hydrogel with a 1:3 ratio of hydroxyethyl cellulose to hyaluronic acid is effective for delivering drugs through the skin to treat acne.
74 citations,
November 2000 in “Archives of Dermatology” Salicylic acid can safely exfoliate and regenerate skin without causing inflammation.
53 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of toxicologic pathology” The project created a standardized system for classifying skin lesions in lab rats and mice.
 17 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic therapy”
17 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic therapy” Different treatments for alopecia areata have unpredictable results and varying success rates.
November 2023 in “Biomolecules” The research showed that Vitamin D and its receptor are important for healthy bones and normal hair and skin in rats.
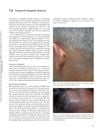 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Temporal triangular alopecia is a lifelong condition with hairless patches on the side of the head that may be present from birth.
 24 citations,
September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
24 citations,
September 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The place where hair is transplanted can affect its growth and survival rates.
 19 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
19 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The protein p53 directly reduces the production of Keratin 17, a skin and hair protein, in rats with radiation dermatitis.
 8 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in dermatology”
8 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in dermatology” The best animal model for studying male-pattern baldness is the stumptailed macaque, not rats or mice.
 3 citations,
January 2016 in “Annals of Dermatology”
3 citations,
January 2016 in “Annals of Dermatology” Minoxidil was the most effective treatment for hair regrowth in rats compared to Aminexil or Kerium.
 January 2018 in “International journal for pharmaceutical research scholars”
January 2018 in “International journal for pharmaceutical research scholars” Meniran extract hair tonic may stimulate hair growth in rats, with the version containing 1% menthol being more effective.
 38 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncologist”
38 citations,
September 2017 in “Oncologist” Scalp cooling can help prevent chemotherapy-induced hair loss with a 50-90% success rate and is safe for patients.
 4 citations,
April 2012 in “Asian-australasian Journal of Animal Sciences”
4 citations,
April 2012 in “Asian-australasian Journal of Animal Sciences” Red deer antler extract may help hair grow faster by increasing a growth protein.
 April 2011 in “한국생물공학회 학술대회”
April 2011 in “한국생물공학회 학술대회” Lotion with fucoidan from brown seaweed improved skin and reduced allergy symptoms in mice with dermatitis.
 August 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
August 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that low-dose acne treatment is most suitable for moderate acne, with high patient satisfaction and low relapse rates.
 9 citations,
July 2011 in “Scientific Reports”
9 citations,
July 2011 in “Scientific Reports” Changes in the HR gene have influenced hair growth and may lead to hair loss conditions in humans.
 268 citations,
April 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
268 citations,
April 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” Niosomes improve minoxidil skin delivery for hair loss treatment.
 36 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
36 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Mice are useful for researching human hair loss and testing treatments, despite some differences between species.
 271 citations,
September 2008 in “Nutrition reviews”
271 citations,
September 2008 in “Nutrition reviews” Vitamin D receptor interacts with certain dietary components to help prevent diseases and regulate hair growth.
 224 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
224 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” The document concludes that understanding hair follicle biology can lead to better hair loss treatments.
 185 citations,
December 2011 in “Molecular and cellular endocrinology”
185 citations,
December 2011 in “Molecular and cellular endocrinology” Skin cells produce and activate vitamin D, which regulates skin functions and supports hair growth.
 178 citations,
May 2006 in “Developmental Dynamics”
178 citations,
May 2006 in “Developmental Dynamics” Jumonji genes are important for development and their mutations can cause abnormalities, especially in the heart and brain.
 158 citations,
August 2011 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders”
158 citations,
August 2011 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders” Vitamin D and its receptor regulate skin functions like cell growth, immunity, hair cycle, and tumor prevention.
 89 citations,
September 2010 in “Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics”
89 citations,
September 2010 in “Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics” The document concludes that understanding the genes and pathways involved in hair growth is crucial for developing treatments for hair diseases.
 81 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of cellular physiology”
81 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of cellular physiology” Mice without the vitamin D receptor gene lose hair due to disrupted hair follicle cycles.























